Fig. 1.
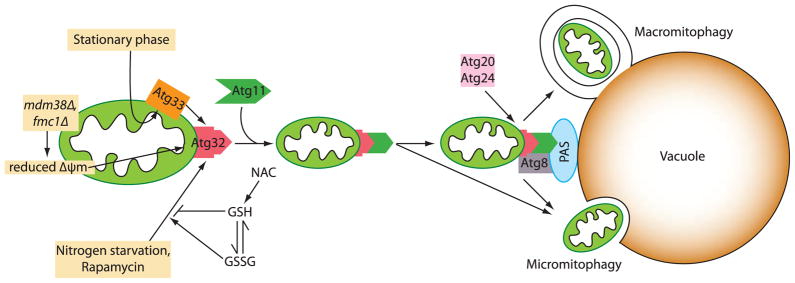
A schematic model of mitophagy in yeast. Mitophagy is induced by a reduction of the mitochondrial membrane potential, nitrogen starvation, rapamycin or entry into stationary phase. The reduced glutathione pool (GSH) inhibits mitophagy. Once mitophagy is induced, the mitochondrial receptor Atg32 binds the adaptor protein Atg11. Atg11 recruits mitochondria to the PAS where Atg32 can bind Atg8 to promote the generation of the phagophore, which encloses the mitochondria. Mitochondria may be delivered into the vacuole via a macroautophagy-like or microautophagy-like mechanism.
