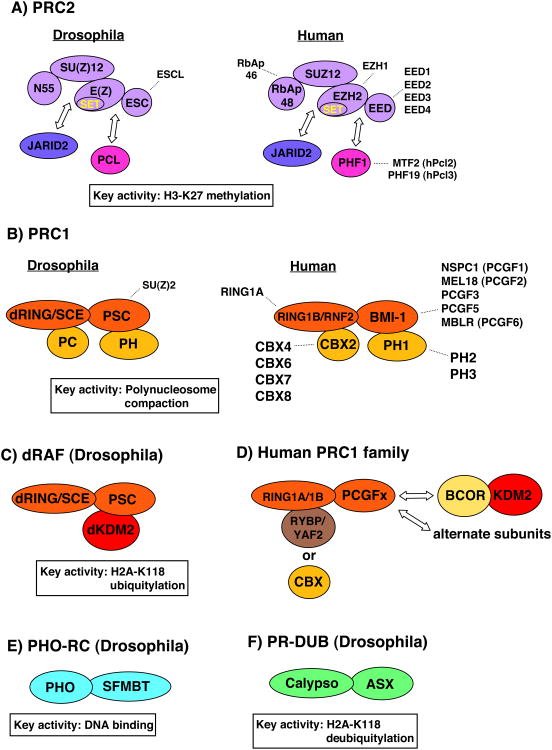
Figure 1. Compositions and activities of PcG complexes.
A) PRC2 family of complexes. Core subunits are in lavendar and arrows depict association of optional subunits. Dashed lines indicate alternative subunits derived from multiple gene copies or protein variants from a single gene. B) and C) PRC1 family of complexes. B) Canonical PRC1 with four core subunits including a PC homolog (CBX in mammals). C) and D) PRC1 variants that contain KDM2 and/or RYBP subunits. In human PRC1 complexes, assembly of RYBP and CBX subunits are mutually exclusive. See (Gao et al., 2012; Gearhart et al., 2006; Lagarou et al., 2008; Tavares et al., 2012) for detailed descriptions of PRC1 variants. Ubiquitylation occurs on H2A-K119 in mammals, corresponding to K118 in Drosophila. E) PHO-RC and F) PR-DUB from Drosophila. Human homologs of PHO (YY1), SFMBT, ASX and Calypso (BAP1) exist and mammalian complexes containing ASXL1/2 and BAP1 have been described (Dey et al., 2012). Mammalian complexes comparable to fly PHO-RC have not been characterized.