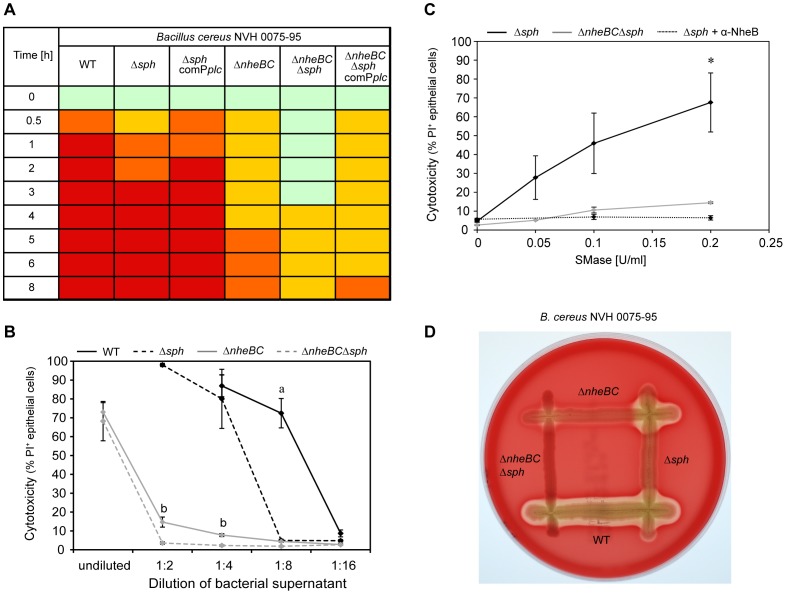
Figure 6. Sph deletion effected B. cereus virulence in vitro.
A. Cytotoxic effect of sterile B. cereus supernatants (1∶4 diluted) on IEC. Intact monolayer (green), cell rounding ≤50% (yellow), cell rounding >50% (orange) and 95–100% cell detachment (red) are indicated. B. Cytotoxic effects of B. cereus supernatant on IEC were analyzed using flow cytometry. Ptk6 cells were treated with various dilutions of bacterial supernatant of B. cereus NVH 0075-95 WT (black line), ΔnheBC mutant (grey line), Δsph mutant (black dashed line) and ΔnheBCΔsph mutant (grey dashed line). Samples were stained with Propidium iodide (PI) for dead epithelial cells and cytotoxicity is expressed in % of PI positive cells as determined by flow cytometric analysis. Cytotoxicity of the Δsph mutant was strongly reduced at a dilution of 1∶8 compared to WT (a, P<0.05). Sph deletion in addition to Nhe inactivation significantly reduced cytotoxicity compared to Nhe inactivation alone (b, P<0.05). Data plotted represent mean values ± SEM (n = 3). C. Cooperative cytotoxic interaction of SMase and Nhe. Addition of various concentrations of recombinant SMase (0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 U/ml) to diluted (1∶16) bacterial supernatants caused significantly higher cytotoxicity against Ptk6 cells when subtoxic Nhe concentrations were present (Δsph supernatant, black line) compared to supernatant without Nhe (ΔnheBCΔsph supernatant, grey line) (*P<0.05). Addition of anti-NheB (1E11) antibody (10 µg/well) neutralizes Nhe activity (Δsph supernatant+α-NheB, black dotted line). Cytotoxicity is expressed in % of PI positive cells and data represent mean values ± SEM (n ≥3). D. CAMP-like test on sheep blood agar demonstrated complementation of extracellular hemolytic activity between B. cereus NVH 0075-95 Δsph and ΔnheBC. Beta-hemolytic activity appeared as cleared zone around the colonies.