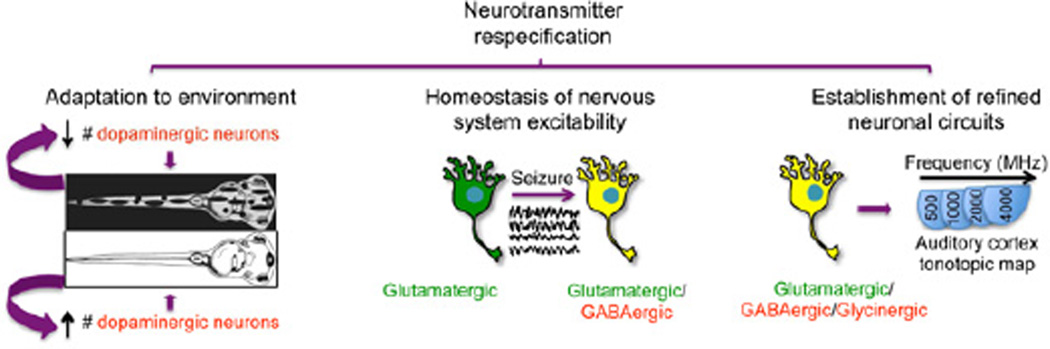
Figure 2. Roles of neurotransmitter respecification.
Activity-dependent changes in specification of the dopaminergic phenotype in the ventral suprachiasmatic nucleus underlie the camouflage behavior of Xenopus laevis larva (left (Dulcis and Spitzer, 2008)). Electrically- or convulsant-induced seizures in rats promote the expression of the GABAergic phenotype in glutamatergic pyramidal hippocampal neurons counteracting the imposed perturbation in the circuit activity (middle (Gomez-Lira et al., 2005)). The developmental coexpression of the glutamatergic phenotype in glycinergic/GABAergic neurons of the olive nucleus is necessary for the establishment of appropriate tonotopic maps in the auditory cortex (right (Noh et al., 2010)).