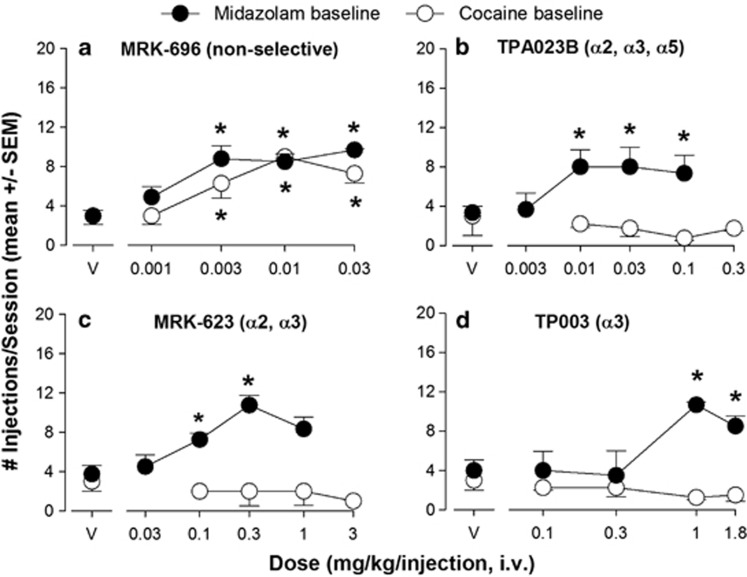
Figure 3.
Differential self-administration of compounds with varying degrees of efficacy GABAA receptor subtypes. (a) Intravenous self-administration of MRK-696 (no differences in efficacy across subtypes) in rhesus monkeys trained under a progressive-ratio schedule of midazolam (0.03 mg/kg/injection; N=4, ‘midazolam baseline') or cocaine (0.03 mg/kg/injection, N=4; ‘cocaine baseline'). Data are mean (± SEM) injections per session, out of a total of 20 injections available in a daily session. Points above ‘V': vehicle tests. Note that *P<0.05 vs vehicle (Bonferroni t-tests). (b) Self-administration of TPA023B (near zero efficacy at α1 subunit-containing receptors, ie, ‘α1-sparing' partial agonist at α2, α3, and α5 subunit-containing receptors) under the same conditions as described for panel a. (c) Self-administration of MRK-623 (near zero efficacy at α1 subunit-containing receptors, ie, ‘α1-sparing' highest efficacy at α2, α3 subunit-containing receptors) under the same conditions as described for panel a. (d) Self-administration of TP003 (zero efficacy at α1 subunit-containing receptors, ie, ‘α1-sparing' highest efficacy at α3 subunit-containing receptors; near zero efficacy at α2 and α5 subunit-containing receptors) under the same conditions as described for panel a. See Figure 1 for receptor subtype selectivity profiles.