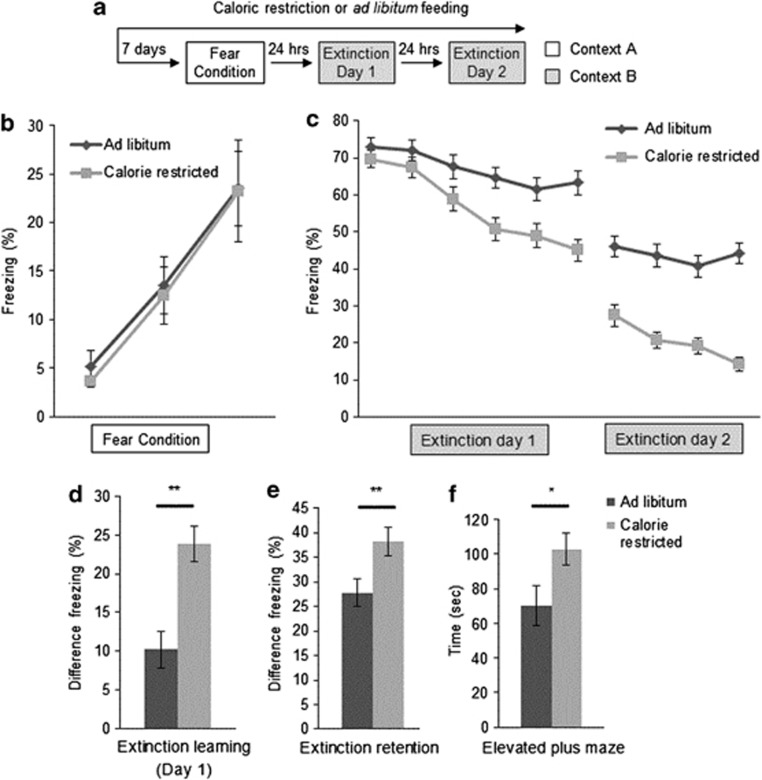
Figure 1.
(a) Fear learning paradigm. CR began 1 week before fear conditioning, and was maintained throughout behavioral testing. (b) Adolescent female mice showed similar levels of freezing during acquisition during each of three tone-shock pairings (n=10, 10). (c) CR improved fear extinction learning on both days of extinction training in adolescent female mice. Each block represents three tones. Extinction day 1 shows all 6 bins; extinction day 2 shows first 4 bins, at which point the groups plateaued. (d) The degree of extinction on day 1, as defined by the difference in freezing between tones 2–5 and 15–18, was significantly enhanced by CR (n=22, 25) as was (e) extinction retention, defined as the difference in freezing between tones 2–5 on extinction day 1 and tones 1–4 on extinction day 2 (n=22, 25). (f) CR also increased time spent in the open arm of the elevated plus maze (n=28, 28). Significance determined with Student's t-test. All results are presented as means±SEM. *p<0.05, **p⩽0.01.