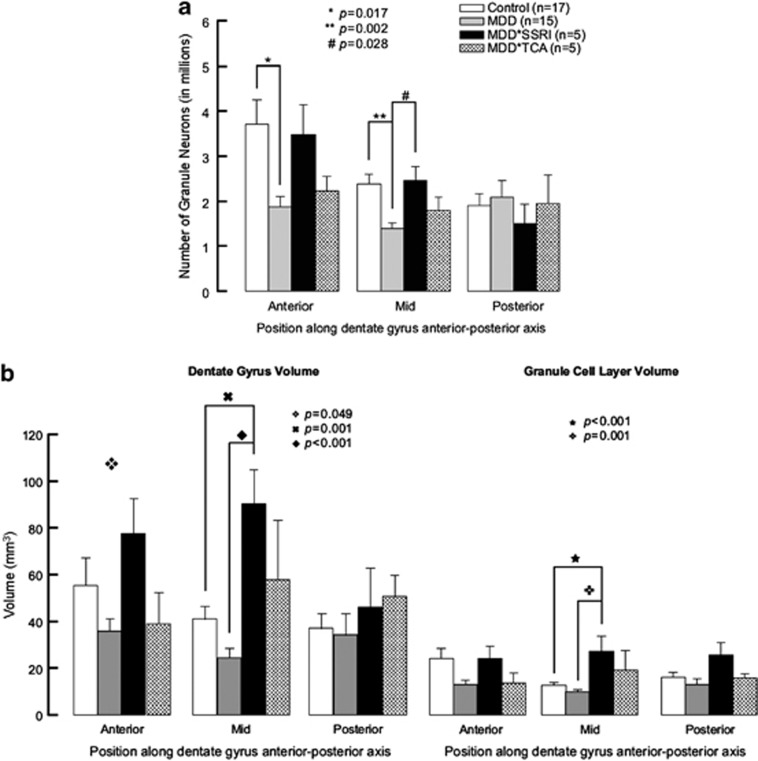
Figure 2.
Granule neuron number and DG and GCL volume along the rostrocaudal axis of the human hippocampus. (a) Untreated subjects with major depressive disorder (MDD) have fewer granule neurons than controls and SRRI-treated MDDs. MDDs show fewer granule neurons (GNs) in the anterior and mid DG compared with controls without psychopathology or treatment. In the mid DG, MDDs treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (MDD*SSRI) have more GNs than untreated MDDs (MDD). In MDDs treated with tricyclic antidepressants (MDD*TCA), GN number does not differ from the other groups in any DG subregion. (b) Dentate gyrus (DG) and granule cell layer (GCL) volume are larger with antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder. ANOVA showed anterior DG volume differs between groups, with no post hoc significance change. Mid DG and GCL volumes are larger in MDDs treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (MDD*SSRI) compared with untreated depressed subjects (MDD) and controls with no psychopathology or treatment. Repeated-measures MANOVA, where anterior and mid position are repeated measures for GCL and DG volumes, showed DG volume is larger in MDD*SSRI vs MDD (p<0.001), MDDs treated with tricyclic antidepressants (MDD*TCA, p=0.020) and controls (p=0.007); GCL volume is smaller in MDD vs controls (p=0.008) and larger in MDD*SSRI vs MDD (p<0.001), MDD*TCA (p<0.001), and controls (p<0.001).