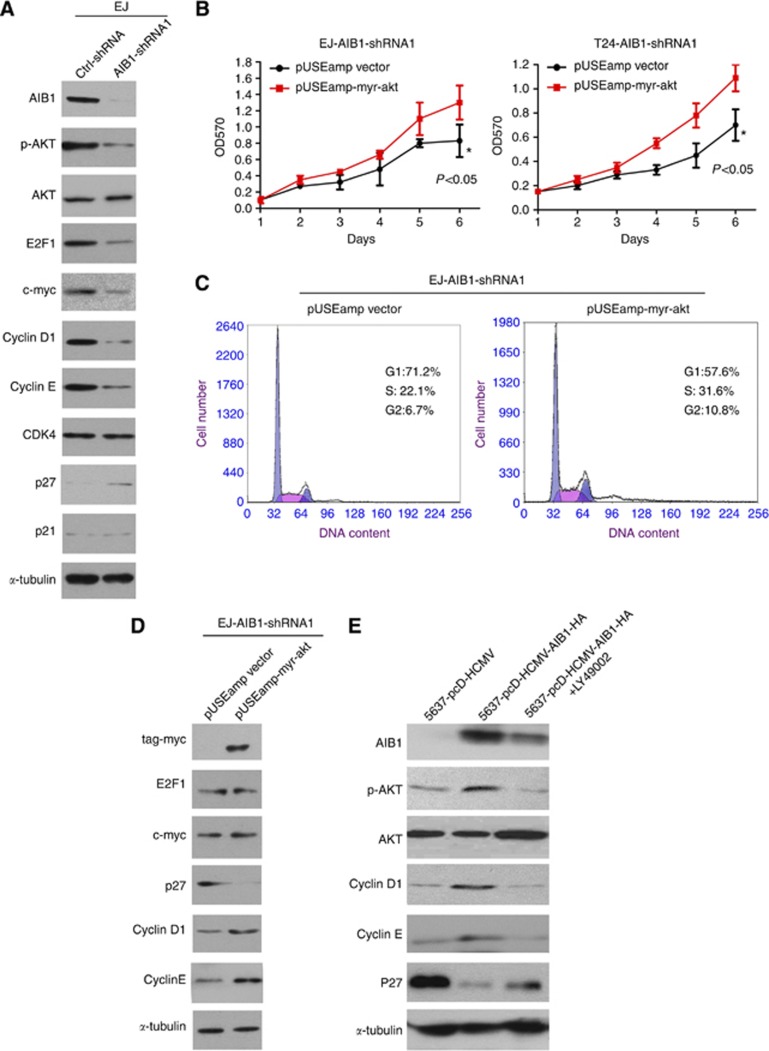
Figure 4.
Depletion of AIB1 altered expression of the AKT pathway and key cell-cycle regulatory proteins. (A) Western blotting revealed that AIB1 knockdown in EJ cells caused a decrease in p-AKT, E2F1, c-myc, cyclin D1, and cyclin E and an increase in p27. (B) Transfection of constitutively activated AKT (myr-AKT) into EJ-shAIB1 and T24-shAIB1 cells restored proliferation, as determined by MTT assay. *P<0.05 by Student's t-test. (C) Upon myr-AKT transfection into EJ-AIB1-shRNA1 cells, the percentage of cells in G1 phase decreased and the percentage in S phase increased. (D) Introduction of myr-AKT into EJ-AIB1-shRNA1 cells restored the levels of E2F1, c-myc, cyclin D1, and cyclin E and reduced the levels of p27 protein compared with control vector. (E) In 5637 cells ectopically expressing AIB1, p27 levels were partially restored, whereas p-AKT, cyclin D1, and cyclin E levels decreased.