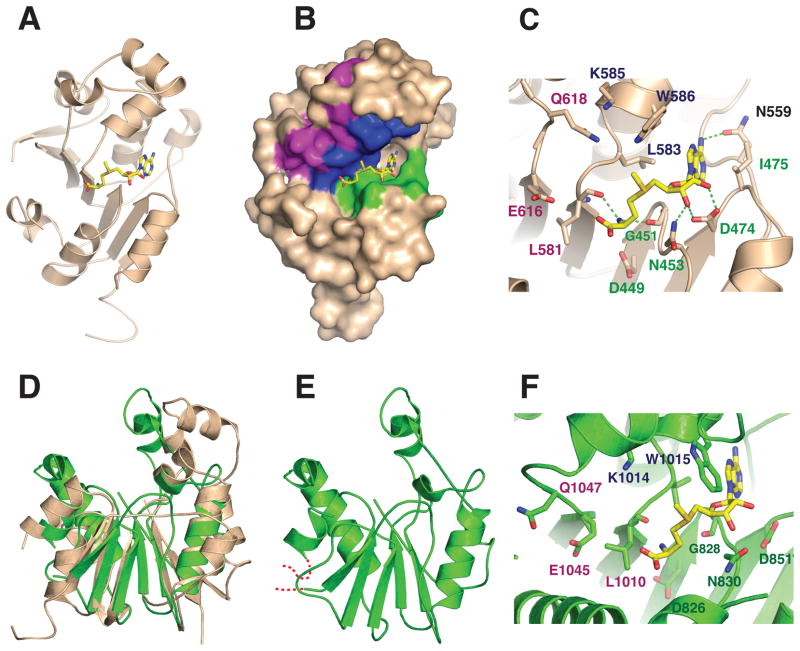
Figure 3.
(A) Cartoon diagram of the X-ray crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human Bin3/MePCE (residues 431–685) bound to S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet) (Yellow). The structure was drawn with PDB coordinates 3G07 using PyMol. (B) Surface representation of human MePCE showing the locations of the consensus AdoMet-binding Motifs I (green), II (blue) and III (purple).6 (C) Active site of human MePCE highlighting hydrogen bond contacts (green dashed lines) between conserved MePCE residues and AdoMet. The position of the donor methyl group of AdoMet suggests that residues from Motifs II and III may be involved in orienting the 7SK RNA substrate for methylation. (D) Superposition of human MePCE and Drosophila Bin3. (E) The Drosophila structure (green) is a homology model based on based on the human structure and refined with the Swiss Model server.21 Residues modeled include aa806–864 and 981–1092. The modeled residues are 47% identical between human and Drosophila Bin-3. The RMS deviation for Cα atom positions is 3.5 Å. (F) Putative active site of Drosophila Bin3 based on homology modeling. Shown are residues that could potentially interact with AdoMet and RNA as in (C).