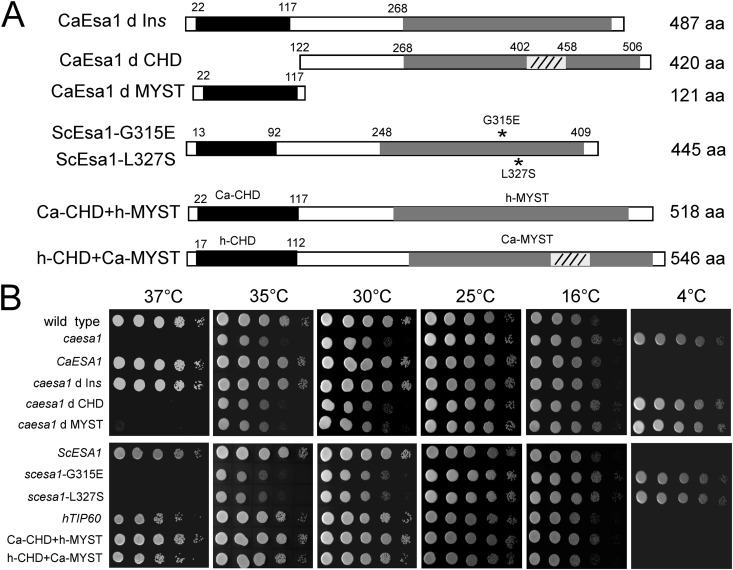
Fig 2.
Expression of both S. cerevisiae ESA1 and human TIP60 can complement the growth defect of the esa1/esa1 mutant in C. albicans. (A) Strategy for ectopic expression. CaEsa1, wild-type C. albicans Esa1; CaEsa1 d Ins, deletion of the insertion region in CaEsa1; CaEsa1 d CHD, deletion of the chromo domain in CaEsa1; CaEsa1 d MYST, deletion of the MYST domain in CaEsa1; ScESA1, wild-type S. cerevisiae Esa1; ScEsa1-G315E, G315E substitution in S. cerevisiae Esa1; ScEsa1-L327S, L327S substitution in S. cerevisiae Esa1; hTIP60, wild-type human TIP60; Ca-CHD+h-MYST, hybrid of C. albicans Esa1 chromo domain and human TIP60 MYST domain; h-CHD+Ca-MYST, hybrid of human TIP60 chromo domain and C. albicans Esa1 MYST domain. (B) Growth of strains on YPD plates at different temperatures. The exponentially growing cells were spotted onto YPD plates and incubated at the temperatures indicated. Ectopic expression vectors pBA-WX1 to pBA-WX10 were introduced into C. albicans esa1/esa1 mutant (CWX3) cells for the complementation assay.