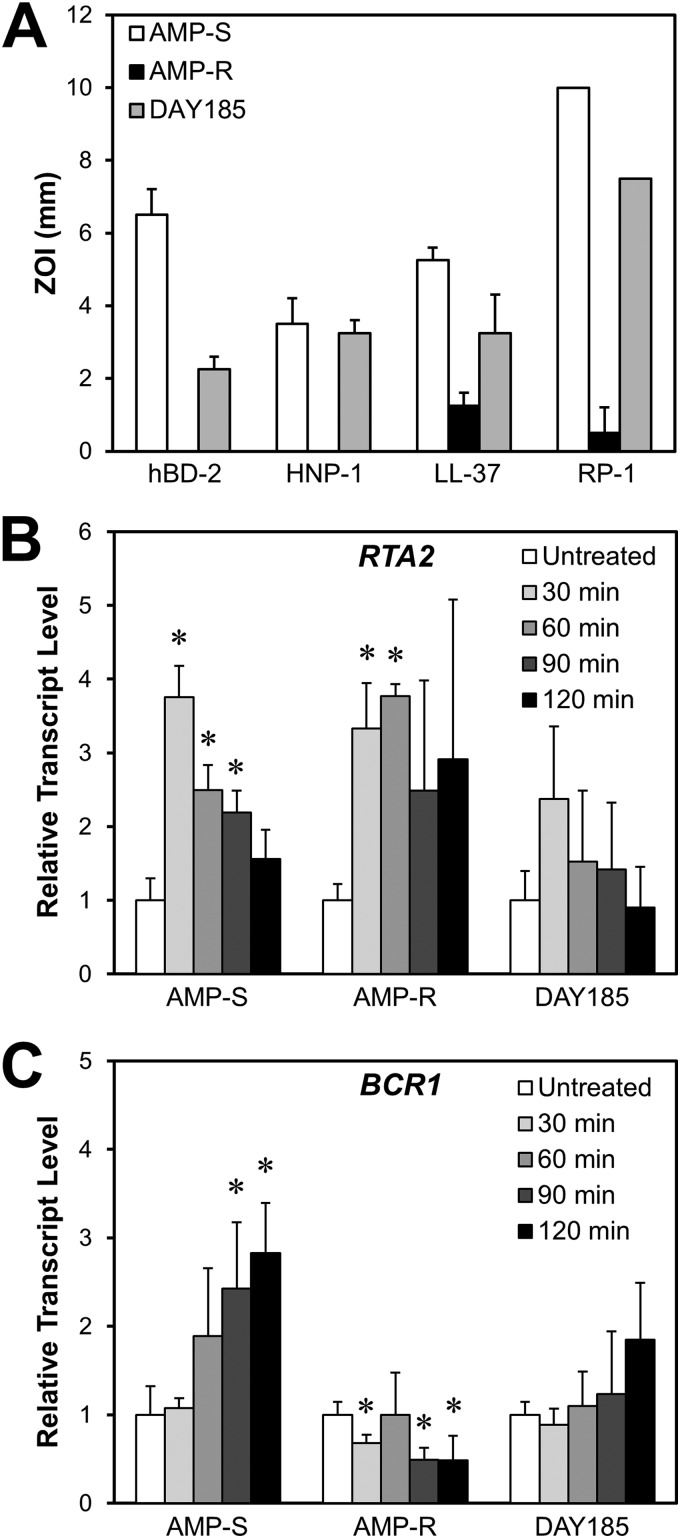
Fig 1.
Comparative antimicrobial peptide susceptibilities and time courses of RTA2 and BCR1 mRNA levels in two C. albicans bloodstream isolates (CA024 [Amps] and CA080 [Ampr]) with differing levels of antimicrobial peptide susceptibility and in the DAY185 reference strain. (A) Susceptibilities of the three C. albicans strains to the indicated antimicrobial peptides were determined by a radial diffusion assay at pH 7.5. Antimicrobial susceptibility was measured as the zone of inhibition (ZOI) after incubation at 30°C for 24 h. Results are means ± standard deviations (SD) from three independent experiments. (B and C) RTA2 (B) and BCR1 (C) transcript levels in the Amps, Ampr, and DAY185 strains after incubation for the indicated time in the presence of a sublethal concentration of RP-1 (2.5 μg/ml for Amps, 100 μg/ml for Ampr, and 5 μg/ml for DAY185). Transcript levels were measured by real-time PCR using ACT1 as the endogenous control gene and normalized to organisms incubated for 60 min in medium without RP-1 (untreated). Results are means ± SD for three biological replicates, each measured in duplicate. *, P < 0.05 compared to cells grown in the absence of RP-1. HNP-1, human neutrophil peptide 1; hBD-2, human β-defensin 2.