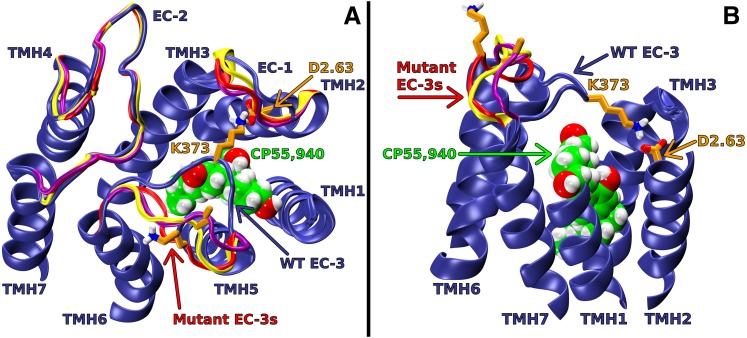
Fig. 5.
Extracellular (EC) loop conformations of WT and D2.63176A, K373A, or D2.63176A-K373A mutant CB1 receptors in the active (R*) state. CP55,940 is shown in green; D2.63176 and K373 are shown in orange; WT EC loops are shown in blue; D2.63176A, K373A, and D2.63176A-K373A mutant EC loops are shown in red, yellow, and purple, respectively. In the WT model, the putative ionic interaction between D2.63176 and K373 has formed; this promotes an EC-3 loop conformation that is pulled over the top of the receptor. In the alanine-substitution models, the putative interaction does not form, and the EC-3 loops are away from the bundle core. (A) Viewpoint is from EC with intracellular (IC) portions of TMHs, IC loops, and the N and C termini omitted to simplify view. (B) Viewpoint is from lipid looking between TMH1 and 7. Note: The IC portions of TMHs, IC loops, EC-1, EC-2, part of TMH1 and 7, and the N and C termini have been omitted here to simplify the view.