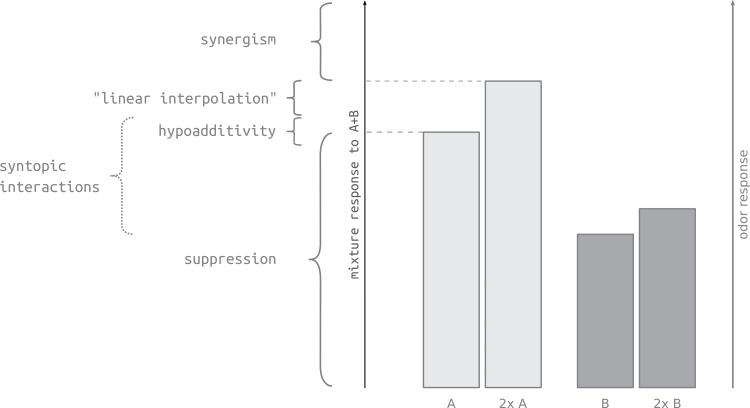
Figure 3.
Scheme of mixture interaction types. Note that different authors use different wording and ranges according to different interaction mechanisms. A mixture response is termed suppressive when it is lower than the response toward the stronger component (A); hypoadditive, when the mixture response is equal to the stronger component (A); synergistic, when the mixture response is higher than the response to the stronger component A at the mixture concentration [A+B] (“2× A” in the figure because in this figure we consider the case of [A] = [B] for simplicity). “Linear interpolation” refers to the case where no interactions happen and the response can be calculated according to Formula 2. Syntopic interaction at the receptor level generally results in responses within the upper suppression range but cannot be calculated precisely without knowledge of the full dose–response curves (Formulas 3 and 4).