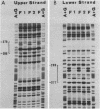
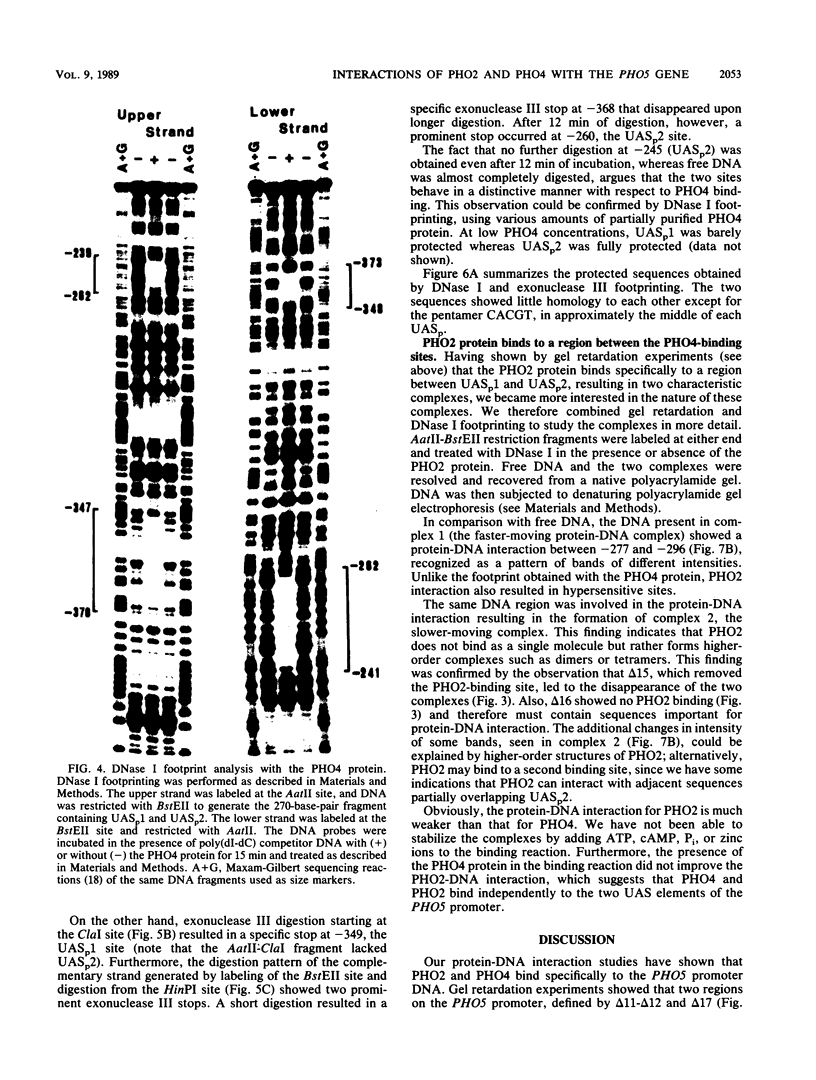
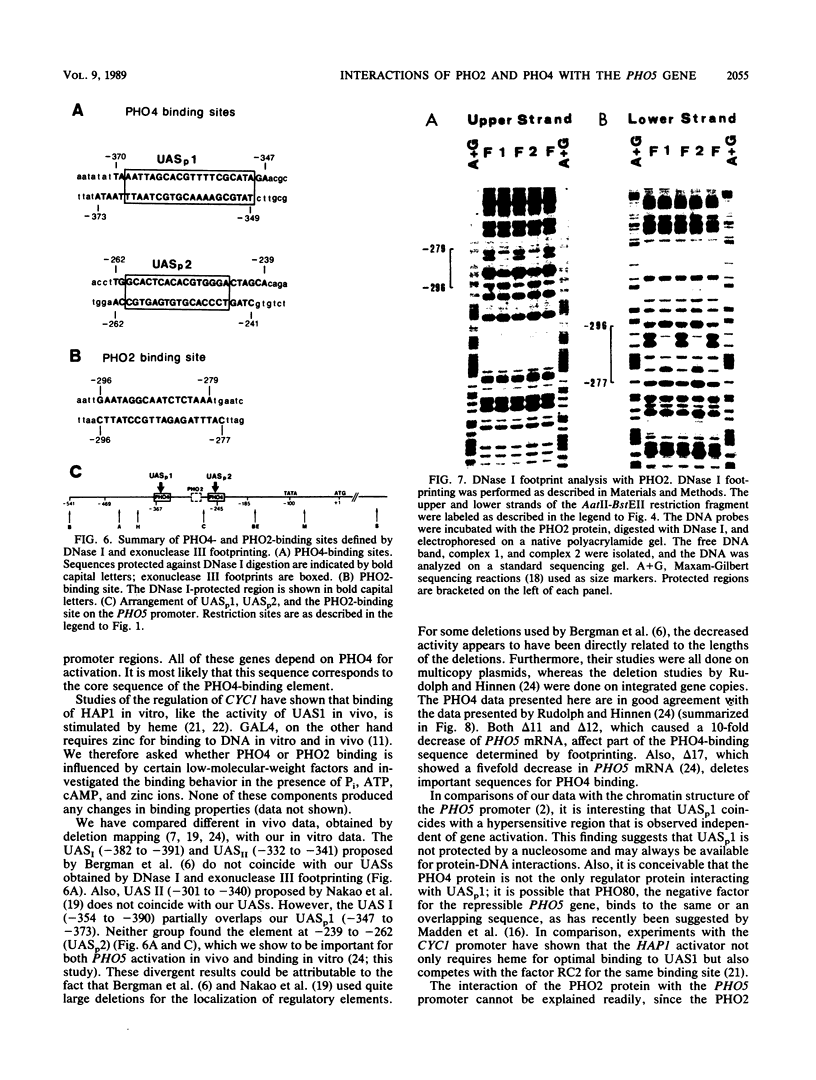
Abstract
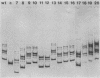
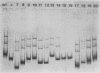
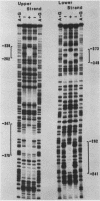
The repressible acid phosphatase gene PHO5 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the two positively acting regulatory proteins PHO2 and PHO4 for expression. pho2 or pho4 mutants are not able to derepress the PHO5 gene under low-Pi conditions. Here we show that both PHO2 and PHO4 bind specifically to the PHO5 promoter in vitro. Gel retardation assays using promoter deletions revealed two regions involved in PHO4 binding. Further characterization by DNase I footprinting showed two protected areas, one located at -347 to -373 (relative to the ATG initiator codon) (UASp1) and the other located at -239 to -262 (UASp2). Exonuclease III footprint experiments revealed stops at -349 and -368 (UASp1) as well as at -245 and -260 (UASp2). Gel retardation assays with the PHO2 protein revealed a binding region that lay between the two PHO4-binding sites. DNase I footprint analysis suggested a PHO2-binding site covering the region between -277 and -296.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almer A., Hörz W. Nuclease hypersensitive regions with adjacent positioned nucleosomes mark the gene boundaries of the PHO5/PHO3 locus in yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2681–2687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almer A., Rudolph H., Hinnen A., Hörz W. Removal of positioned nucleosomes from the yeast PHO5 promoter upon PHO5 induction releases additional upstream activating DNA elements. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2689–2696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. T., Styles C., Fink G. R. Multiple global regulators control HIS4 transcription in yeast. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):874–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3303332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa W., Meyhack B., Rudolph H., Schweingruber A. M., Hinnen A. Structural analysis of the two tandemly repeated acid phosphatase genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7721–7739. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., Kramer R. A. Modulation of chromatin structure associated with derepression of the acid phosphatase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7223–7227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., McClinton D. C., Madden S. L., Preis L. H. Molecular analysis of the DNA sequences involved in the transcriptional regulation of the phosphate-repressible acid phosphatase gene (PHO5) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6070–6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., Stranathan M. C., Preis L. H. Structure of the transcriptionally repressed phosphate-repressible acid phosphatase gene (PHO5) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):38–46. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R. The yeast regulatory gene PHO2 encodes a homeo box. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):339–340. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. Genetic evidence that zinc is an essential co-factor in the DNA binding domain of GAL4 protein. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):353–355. doi: 10.1038/328353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Hayashi N., Toh-e A., Banno I., Oshima Y. Structural characteristics of the PHO8 gene encoding repressible alkaline phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1987;58(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren R., LeVitre J., Bostian K. A. Isolation of the positive-acting regulatory gene PHO4 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain M., De Wilde M., Hilger F. Isolation, physical characterization and expression analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae positive regulatory gene PHO4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):3059–3073. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden S. L., Creasy C. L., Srinivas V., Fawcett W., Bergman L. W. Structure and expression of the PHO80 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2625–2637. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao J., Miyanohara A., Toh-e A., Matsubara K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae PHO5 promoter region: location and function of the upstream activation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2613–2623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Arcangioli B., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator competes with the factor RC2 for binding to the upstream activation site UAS1 of the CYC1 gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90750-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Stanssens P., Fiers W. Plasmid vectors for high-efficiency expression controlled by the PL promoter of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H., Hinnen A. The yeast PHO5 promoter: phosphate-control elements and sequences mediating mRNA start-site selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1340–1344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengstag C., Hinnen A. A 28-bp segment of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PHO5 upstream activator sequence confers phosphate control to the CYC1-lacZ gene fusion. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90399-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengstag C., Hinnen A. The sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene PHO2 codes for a regulatory protein with unusual aminoacid composition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):233–246. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]