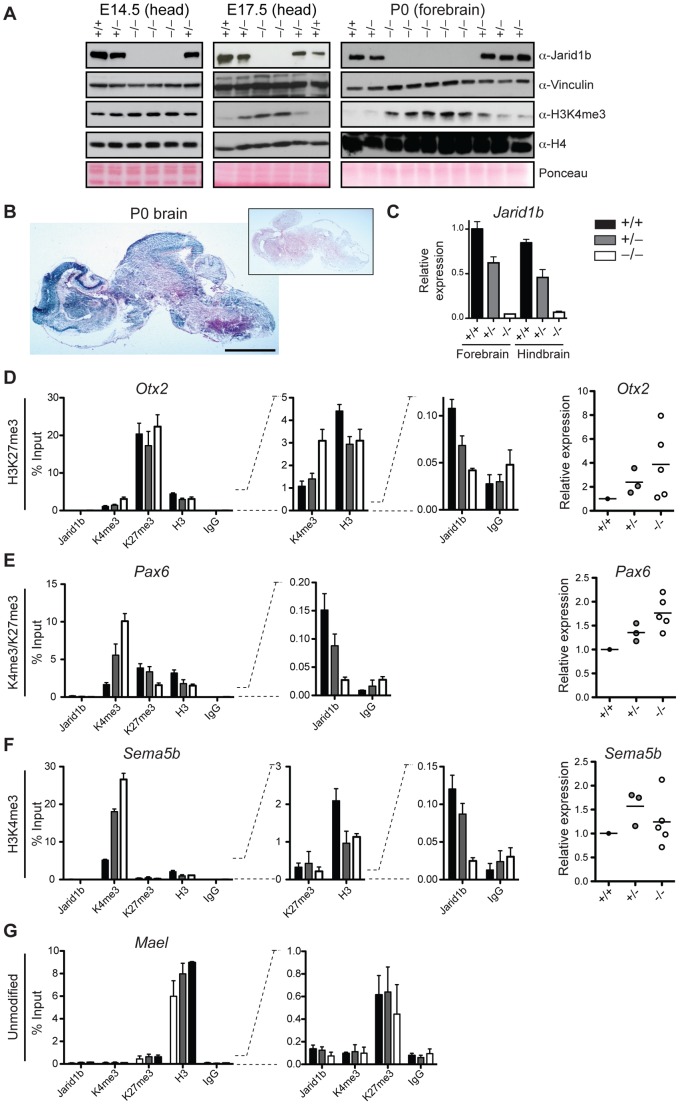
Figure 7. Loss of Jarid1b leads to increased global levels of H3K4me3 and higher expression of key developmental regulators during embryogenesis.
(A) Immunoblots for Jarid1b and H3K4me3 of Jarid1b embryos at different developmental stages. Vinculin, H4 and Ponceau serve as loading controls. (B) Staining for β-galactosidase on sections of P0 brains representing Jarid1b expression. Staining of a wild-type brain is shown as negative control (boxed inset). Scale bar, 2 mm. (C) Expression of Jarid1b in fore- and hindbrains of wild-type, heterozygous and knockout newborns (normalized to β-actin). (D–G) Left: ChIP-qPCR for Jarid1b, H3K4me3, H3K27me3, H3 and IgG in forebrains of P0 pups. Error bars represent S.D. of three PCR amplifications. Right: Expression of indicated genes in forebrains analyzed by RT-qPCR (normalized to β-actin). Each dot represents an individual embryo. MaeI expression was below detection. One representative gene is shown for each chromatin state: (D) H3K27me3, (E) H3K4me3/H3K27me3, (F) H3K4me3 and (G) unmodified.