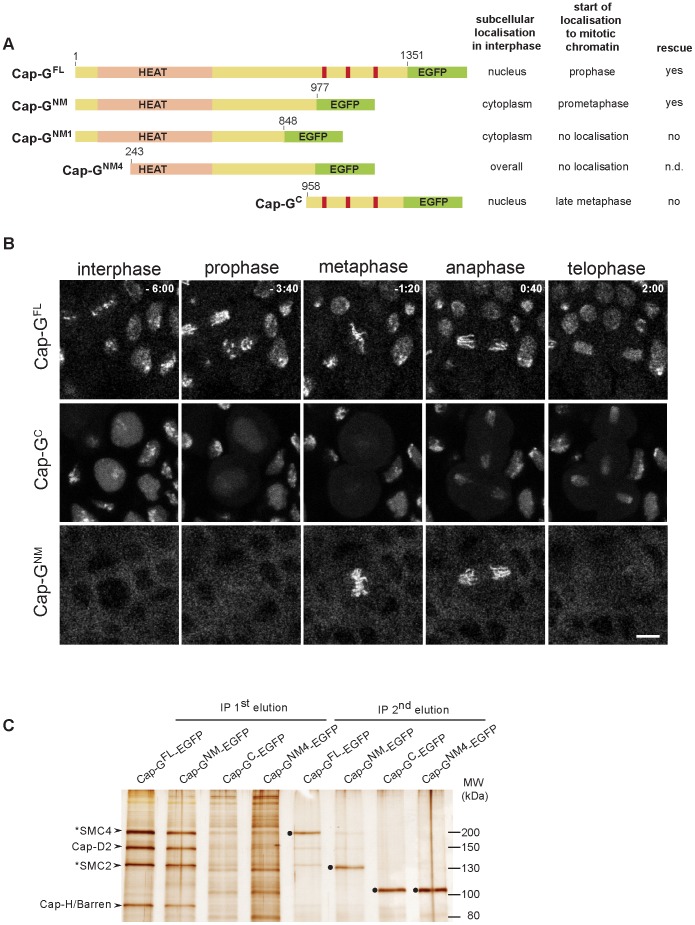
Figure 2. The N-terminal two-thirds of Cap-G are sufficient for interaction with chromatin and condensin I subunits.
(A) Left panel. Schematic drawing of the analyzed EGFP-fused Cap-G-fragments. Full-length Cap-G (Cap-GFL) encompasses 1351 aa. HEAT-repeats (pale pink) are predicted by SMART between residues 50 and 553, and nuclear import signals (red bars) are predicted by PSORT at aa positions 1072, 1162 and 1210. Right panel. The localization characteristics of the Cap-G constructs as well as their ability to complement the lethality associated with Cap-G loss-of-function mutants is indicated. (B) Subcellular localization and chromatin association of different EGFP-fused Cap-G-fragments observed in living embryos progressing through epidermal mitosis14. Expression of different UAST-Cap-G-EGFP transgenes was driven by α4-tub-GAL4-VP16. Cap-GC-EGFP is enriched inside the nuclei during interphase but does not associate with chromatin during early stages of mitosis. In contrast, Cap-GNM-EGFP is mainly cytoplasmic during interphase and associates with mitotic chromatin immediately after NEBD. Individual frames of representative time lapse movies are shown with time points indicated in min (t = 0, anaphase onset). Scale bar is 5 µm. (C) Extracts from 3–6 h old embryos expressing various EGFP-fused Cap-G-fragments driven by α4-tub-GAL4-VP16 were subjected to immunoprecipitation with rabbit-anti-EGFP antibodies. Bound proteins were eluted in two steps with increasing stringency. Precipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to silver staining. The identity of Cap-H/Barren and Cap-D2 was confirmed by immunoblotting, SMC2 and SMC4 were assigned according to their expected molecular weight (indicated by asterisks). The condensin I subunits were efficiently precipitated by both Cap-GFL-EGFP and Cap-GNM-EGFP and were eluted during the first step (IP 1st elution), while they were not significantly precipitated by Cap-GNM4-EGFP and Cap-GC-EGFP. The second elution step (IP 2nd elution) mainly reveals the recovery of the EGFP-fused Cap-G-fragments (filled circles). Note that Cap-GFL-EGFP and Cap-GNM-EGFP migrate at the same position in the SDS-polyacrylamide gel as SMC4 and SMC2, respectively.