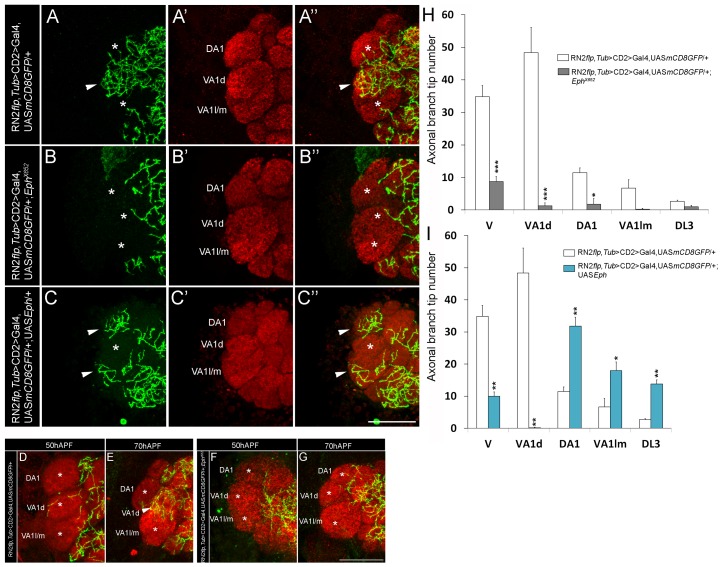
Figure 5. Perturbation in Levels of Eph signaling leads to defective glomeruli-specific positioning of the terminal of the CSDn.
(A-A″, H) Innervation pattern of the axonal terminals of the CSDn (green) in glomeruli VA1l/m, VA1d and DA1 (anti-Brp in red) in control adults is shown (n≥6). (B-B″, H) In Eph null animals, axonal terminals of the CSDn show overall reduction in their AL innervation. This defect is pronounced in glomeruli which normally receive more innervations from the CSDn (VA1d (n = 4, p<0.001), VA1l/m (n = 4, p = 0.127), DA1 (n = 4, p = 0.025), DL3 (n = 4, p = 0.745) and V (n = 4, p<0.001). (C-C″, I) Targeted expression of Eph in the CSDn results in exquisite reversal of the terminal arborization pattern in these glomeruli compared to controls; terminals preferentially target VA1l/m (n = 5, p = 0.002), DA1 (n = 5, p<0.001), DL3 (n = 5, p = 0.003) and avoid glomerulus VA1d (n = 5, p<0.001). (H–I) Quantification of total axonal branch tip number is plotted in a histogram. Asterisks indicate glomeruli with fewer innervations and arrowhead indicates glomerulus with more innervations from the CSDn. A one-way repeated measure ANOVA test was performed to assess significant difference between the genotypes (F = 27.341, P<0.001). All pairwise multiple comparisions were performed using Fisher LSD method. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.0001; n.s. (not significant), p>0.05. Scale bar = 20 µm. (D–G) Glomeruli-specific innervation of axonal terminals is achieved by directed growth of axonal terminals of the CSDn. Terminal arbors of the CSDn in (D–E) control (RN2flp, tub>CD2>Gal4, UASmCD8GFP/+) and (F–G) Eph mutant animals (RN2flp, tub>CD2>Gal4, UASmCD8GFP/+; EphX652). Developmental profile of the axonal terminals of control CSDn at (D) 50 hAPF and (E) 70 hAPF is shown. (D) At 50 hAPF, very few axonal terminals of the CSDn can be seen extending to region of the AL where VA1l/m, VA1d, DA1 and DL3 are located. (E) Adult-like pattern of glomeruli-specific innervation of axonal terminals is apparent at 70 hAPF where high innervation of VA1d and low innervation of VA1l/m and DA1 by the CSDn terminals is seen. (F) At 50 hAPF, axonal terminals of the CSDn in Eph null mutants can be seen near the region of AL where the above-mentioned four glomeruli are located but (G) fail to innervate these glomeruli even at 70 hAPF. Asterisks indicate glomeruli with fewer innervations and arrowhead indicates glomerulus with more innervations from the CSDn. Scale bar = 20 µm.