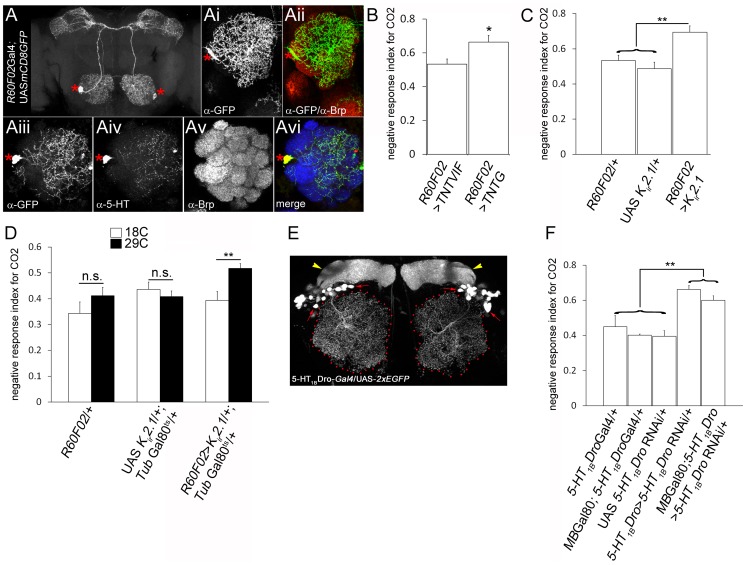
Figure 6. CSDn modulates odour-guided behaviour.
The pair of CSDn is specifically labeled by R60FO2Gal4. Targeted expression of GFP using R60FO2Gal4 (R60F02Gal4/+; UAS mCD8GFP/+) shows a pair of neurons with anatomy characteristic of the CSDn and (Ai–Aii) innervations to the antennal lobe (Brp in red; GFP in green). (Aiii–vi) The neurons labeled by R60F02 co-express 5-HT (red) indicating it is indeed the CSDn (green; Brp in blue). Asterisks indicate cell body of the CSDn. (B–F) The CSDn modulates olfactory response of adult Drosophila towards CO2. (B) Suppression of evoked synaptic transmission by targeted expression of tetanus toxin light chain (TNTG) in the CSDn (R60F02Gal4/+; UAS TNTG/+, n = 10, p = 0.017) leads to an increase in CO2 avoidance index compared to control animals (R60F02Gal4/+; UAS TNTVIF/+, n = 12). (C) Similar increase in CO2 sensitivity is observed upon suppression of CSDn excitability by targeted Kir2.1 expression (R60F02Gal4/+; UAS Kir2.1/+, n = 11, p<0.01 compared to controls) in the CSDn. (D) CSDn function is required in the adults for modulating olfactory behaviour. Adult-specific expression of Kir2.1 in the CSDn is achieved by rearing animals (R60F02Gal4/+; UAS Kir2.1/+; Tub-Gal80ts/+) at 18°C throughout development (white bars in D) and then shifting to 29°C after eclosion (black bars in D). Adult-specific suppression of CSDn excitability results in increased CO2 avoidance (n = 17; p = 0.006). (E) In a reporter line for serotonin receptor 5-HT1BDro (5-HT1BDro-Gal4/+; UAS-2xEGFP/+), a group of local interneurons are labeled (red arrows) along with mushroom bodies (yellow arrowheads). (F) RNAi-mediated knock down of 5-HT1BDro in the 5-HT1BDro expression domain (5-HT1BDro-Gal4/+; UAS-5-HT1BDroRNAi/+, n = 11) results in increased CO2 sensitivity (p<0.05 compared to all control genotypes, n>7). 5-HT1BDro expression outside the mushroom bodies, likely in the AL, may be necessary for CO2 sensitivity as blocking 5-HT1BDroRNAi expression in mushroom body neurons (MB-Gal80/+; 5-HT1BDro-Gal4/+; UAS-5-HT1BDroRNAi/+, n = 14) does not ameliorate increased CO2 sensitivity (p = 0.12 compared to 5-HT1BDro-Gal4/+; UAS-5-HT1BDroRNAi/+, n = 11) and animals exhibit increased CO2 avoidance (p<0.01 compared to all control genotypes, n>7). Significance was assessed by Mann-Whitney test. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.0001; n.s. (not significant), p>0.05.