Figure 7. Glomerular-specific innervation pattern of the CSDn is relevant for odour-specific modulation of odour-guided behavior.
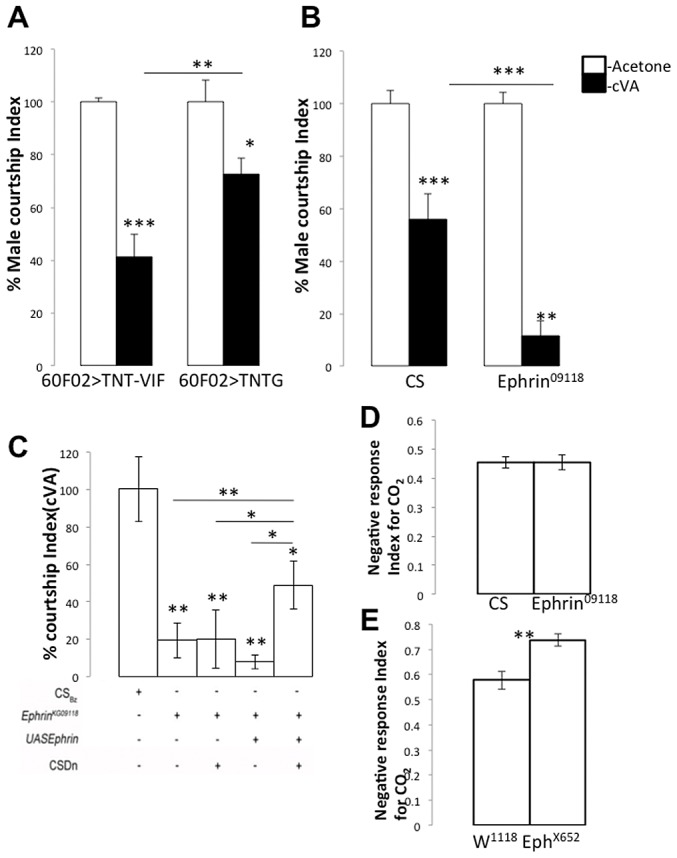
(A) Targeted expression of tetanus toxin light chain in the CSDn (R60F02Gal4/+; UAS TNTG/+, n = 14, p = 0.028) leads to an increase in relative male courtship index towards cVA-treated virgin females compared to controls (R60F02Gal4/+; UAS TNTVIF/+, n = 16) which implies decreased sensitivity towards cVA in test animals. Now to test the effect of increasing arbors of the CSDn in cVA sensitive glomeruli we tested courtship index of EphrinKG09118. (B) EphrinKG09118 males are more sensitive to cVA as exhibited by highly reduced courtship towards cVA-treated females (n = 25, p<0.001) compared to control males (n = 17). (C) Targeted Ephrin expression in the CSDn in an Ephrin mutant background (RN2flp, tub>CD2>Gal4, UASmCD8GFP/UAS Ephrin; EphrinKG09118 in which both the CSD neurons were labeled; n = 26) results in partial rescue of the cVA sensitivity compared to the Ephrin mutant males (p = 0.004). . On the other hand, (D) CO2 sensitivity of EphrinKG09118 (n = 12; p = 0.98) is comparable to controls (n = 19). (E) EphX652 animals show increased avoidance (n = 8; p = 0.003) towards CO2 compared to controls (n = 10). As shown earlier, in EphX652 the CSDn innervations to V glomerulus are reduced while in Ephrin hypomorphs, these are comparable to controls. The courtship Index towards cVA treated females are normalized to the respective males Courtship Index towards Acetone (Mock) treated Virgin females. Significance was assessed by Mann-Whitney test. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.0001; n.s. (not significant), p>0.05.
