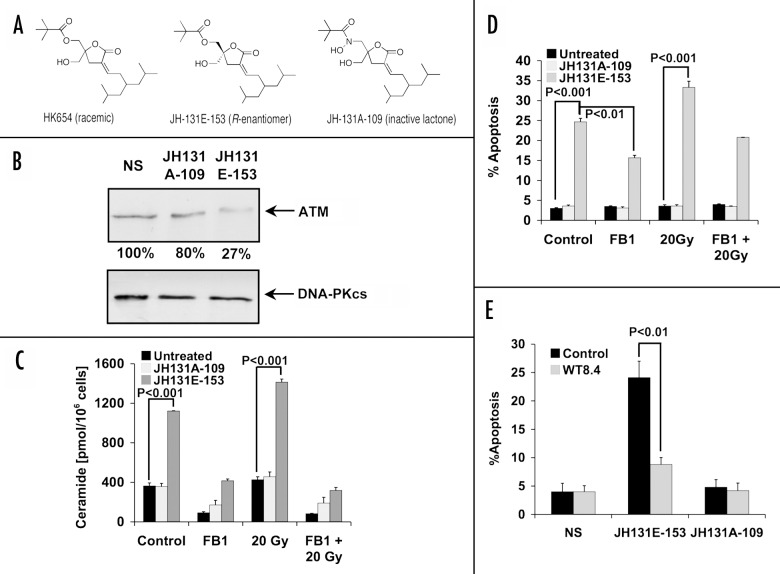
Figure 4. Effect of specific PKCα activator DAG-lactone on LNCaP cells. (A) Chemical structures are shown for the racemic mixture (HK654) used previously,2 its active R-enantomer (JH-131E-153), and an inactive analog (JH-131A-109). (B) western blot analysis of ATM levels following 16 h incubation with either DAG-lactone or control. The relative abundance of ATM is shown as percent of NS controls. DNA-PKcs levels were used as a loading control. The results are representative of three experiments. (C) LNCaP cells were treated for 16 h with 10 μM of active DAG-lactone JH-131E-153, or inactive analog JH-131A-109 prior to irradiation with 20 Gy. Where indicated, FB1 (40 μM) treatment was applied three h before irradiation. Ceramide levels were measured 12 h post-irradiation and the bars represent s.d. values. These experiments were repeated three times. (D) Each DAG-lactone was added to the cells as described in (C). Following an additional 24 h, apoptotic cells were determined as in Figure 2D. The results are mean average ± s.d. of duplicate determinations from three experiments. (E) Active and inactive DAG-lactones (10 μM) were added to either wild-type stably-transfected LNCaP cells (WT8.4) or to empty-vector transfected cells (Control) and apoptosis was quantified 48 h later. The results are the mean average ± s.d. of duplicate determinations from three experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.