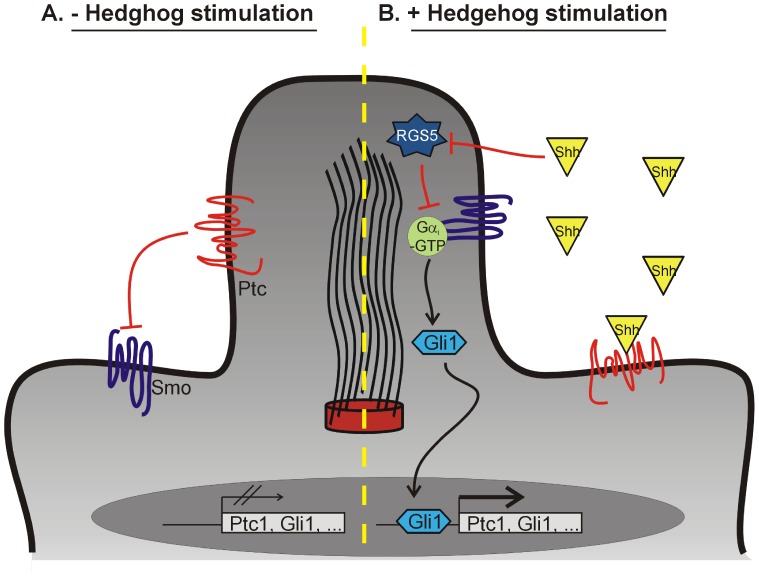
Figure 4. The hedgehog-mediated signaling mechanism in the absence (A) and presence (B) of Shh.
RGS5 inhibits Shh-mediated signaling. RGS5 functions to inhibit signaling down-stream of Smo by hydrolyzing Gαi-GTP. In the absence of Shh, RGS5 inhibits Smo-dependent signaling by inactivating Gαi and blocking the expression of the Gli transcription factors and Ptc co-receptors. In the presence of Shh, RGS5 expression is repressed, leading to the potentiation of the activation of Gli and Ptc expression.