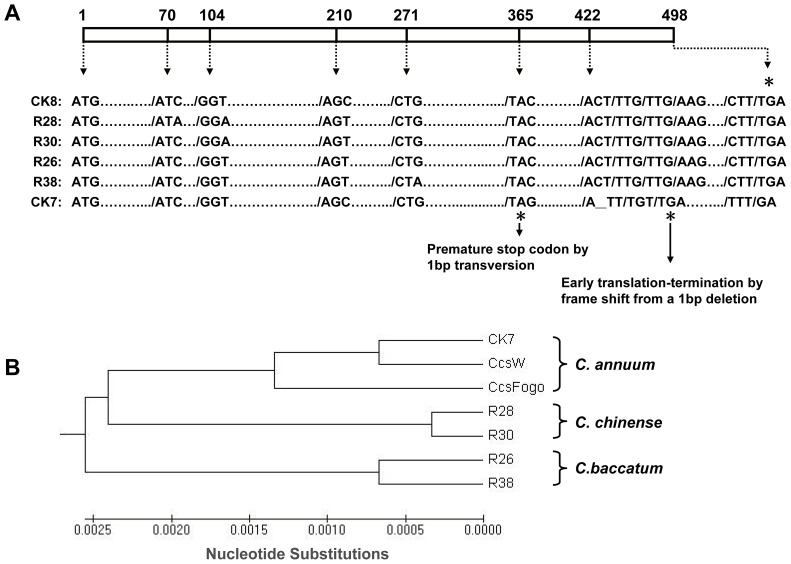
Figure 4. Comparisons of the Ccs coding sequences in the indicated Capsicum varieties.
(A) Schematic representation of the mutations in Ccs among different cultivars. The nucleotide sequences were aligned, and the resulting missense mutations in the amino acid sequence are marked with asterisks. The 1-bp deletion in the coding sequence, which leads to early translation-termination, is underlined in the CK7 sequence. ATG and TGA indicate the start and stop codons, respectively. (B) Phylogenetic tree of the Ccs gene generated by multiple alignments of the coding sequence. The sequence of CcsW, which served as the positive control, was obtained from the NCBI (Accession: ×76165), and the sequence of CcsFogo was obtained from Guzman et al. [11] (GenBank GU122933).