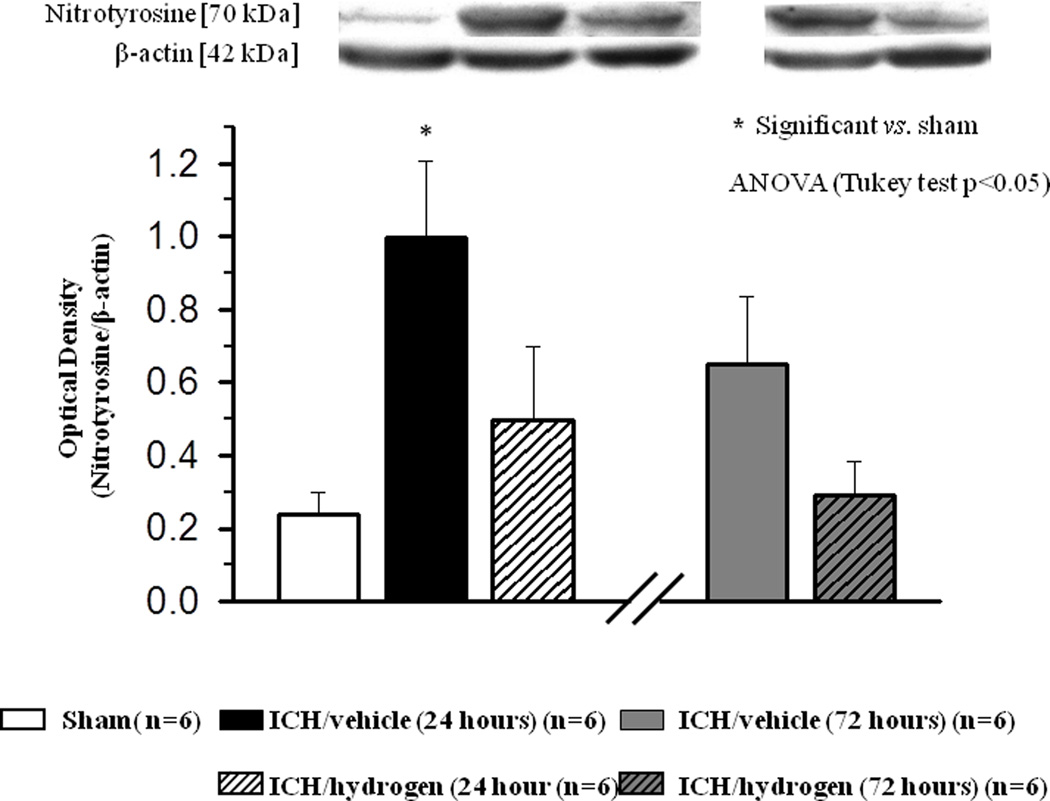
FIGURE 9.
At 24 hours after inducing of intracerebral hemorrhage, significant accumulation of nitrotyrosine was observed in brain of animals after intracerebral hemorrhage ( N=6) compared to sham operated animals (
N=6) compared to sham operated animals ( N=6). Hydrogen inhalation decreased intracerebral hemorrhage induced accumulation of nitrotyrosine at 24 hours (
N=6). Hydrogen inhalation decreased intracerebral hemorrhage induced accumulation of nitrotyrosine at 24 hours ( ). At 72 hour after inducing of intracerebral hemorrhage, hydrogen treatment showed a strong tendency to diminish nitrotyrosine accumulation in brain of hydrogen treated (
). At 72 hour after inducing of intracerebral hemorrhage, hydrogen treatment showed a strong tendency to diminish nitrotyrosine accumulation in brain of hydrogen treated ( N=6) compared to untreated (
N=6) compared to untreated ( N=6) animals. * significant vs. sham, # significant vs. vehicle, p<0.05 ANOVA, Tukey test
N=6) animals. * significant vs. sham, # significant vs. vehicle, p<0.05 ANOVA, Tukey test