Figure 4. Cellular uptake of liposomes.
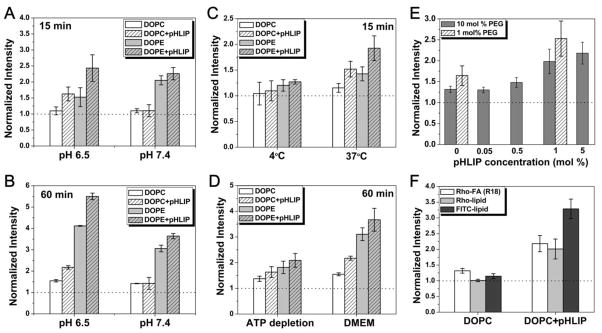
A549 cells in suspension were treated with fluorescently labeled liposomes (DOPC or DOPE) with or without pHLIP in liposome coat under various conditions. Cellular uptake of fluorescent liposomes was accessed by counting of fluorescent cells on a cellometer. All data were normalized to the fluorescence intensity of untreated cells (dotted line). (A–B) pH- and pHLIP-dependent cellular uptake of liposomes is shown. Cells were incubated with R18-labeled liposomes with (‘5:5’) or without (‘0:10’) pHLIP in liposome coat at pH 7.4 or 6.5 in PBS for 15 min (A) or in serum-free DMEM for 60 min (B). (C–D) Cells were incubated with R-18 labeled liposomes at pH 6.5 in PBS at 4°C or 37°C for 15 min (C) and in serum-free DMEM or ATP depletion medium at 37°C for 60 min (D). Low temperature and ATP depletion medium are used to reduce endocytotic uptake. (E) Cellular uptake of DOPC liposomes (pH 6.5, DMEM, 37°C, 60 min) depends on amount of pHLIP and PEG in liposome coat. (F) The pH- and pHLIP-dependent cellular uptake does not depend on choice of fluorescent lipids. Liposomes (‘5:5’ DOPC) containing different fluorescent lipids—Rho-FA (R18), Rhodamine-PE (Rho-lipid), or Fluorescein-DHPE (FITC-lipid)—were incubated with cells (pH 6.5, DMEM, 37°C, 60 min), and pHLIP-dependent fluorescence increase was observed in each case.
