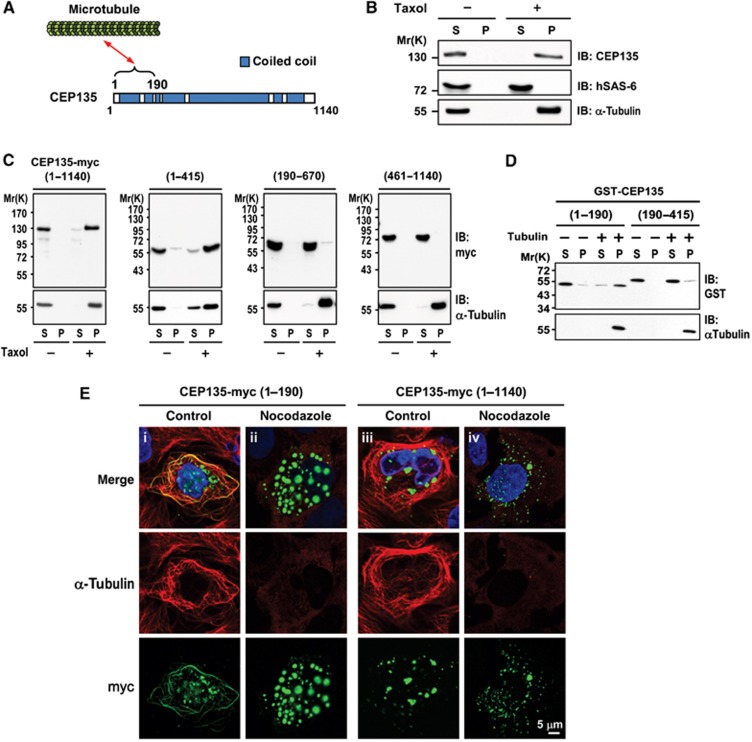
Figure 3.
CEP135 directly binds to microtubules. (A) Schematic of the interaction between CEP135 and microtubules. (B) CEP135, but not hSAS-6, co-precipitates with microtubules. HEK293T cells were lysed in lysis buffer in the presence or absence of Taxol. The cell lysates were centrifuged, separated into supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions, and analysed by IB using the indicated antibodies. (C) Full-length and the N-terminal region of CEP135-myc (residues 1–415) co-precipitates with microtubules. HEK293T cells were transfected with various myc-tagged CEP135 truncation mutants. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were lysed and analysed as described in (B). (D) CEP135 directly binds to microtubules. Purified tubulins were incubated with the indicated GST-tagged recombinant CEP135 proteins in the presence of Taxol. The supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were analysed by IB. (E) CEP135-myc (residues 1–190) binds to microtubules in vivo, and this MT binding is destabilized by nocodazole treatment. U2OS cells were transfected with CEP135-myc (1–190) or full-length CEP135 (1–1140). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were treated without (control) or with nocodazole (2.5 μM) for 1 h, and then analysed by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy using the indicated antibodies.