Figure 2. Effects of t-ACPD on sEPSCs.
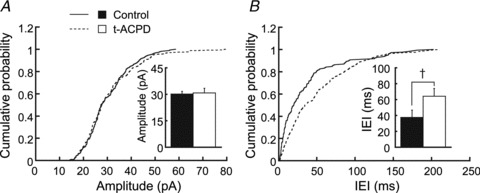
sEPSCs were recorded at −83 mV in artificial cerebrospinal fluid with bicuculline (40 μm). t-ACPD prolonged the IEI but did not affect the amplitude of sEPSCs (n = 189 control events and 174 in t-ACPD). A and B are the cumulative distribution of amplitudes and IEIs of sEPSCs, respectively. Bar graphs show averages in the control and after 3 min in t-ACPD. The difference was significant for IEI (n = 5, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, P < 0.01). IEI, inter-event interval; sEPSC, spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current; t-ACPD, (±)-1-aminocyclopentane-trans-1,3-dicarboxylic acid. †P < 0.01.
