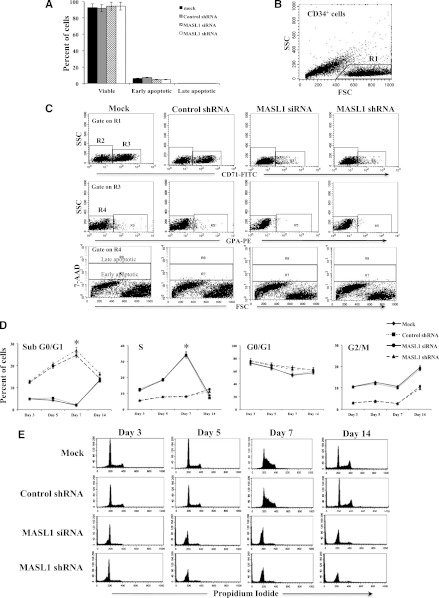
Figure 4.
MASL1 knockdown in CD34+ cells does not alter cell survival within the CD71+ GPA- subpopulation at day 3 of EPO-induced erythroid differentiation but causes cell-cycle arrest in all CD34+ cells during erythroid differentiation. (A) Mean percentages from flow cytometry analysis of 7-AAD- (viable), 7-AADdim (early apoptotic), and 7-AADbright (late apoptotic) in mock-, control shRNA-, MASL1 siRNA-, or MASL1 shRNA-transfected CD71+GPA- subpopulation cells at day 3 of EPO-induced differentiation. Error bars represent the SD from 3 individual experiments. (B) Scattergram of forward scatter (FSC) vs right-angle side scatter (SSC), to allow gating on CD34+ cells by excluding cell debris (R1). (C) Representative scattergram for mock-, control shRNA-, and MASL1-knockdown CD34+ cells of SSC vs anti-CD71 fluorescence gated on R1 to allow gating on CD71- (R2) or CD71+ (R3). (Middle) representative scattergram for mock-, control shRNA-, and MASL1-knockdown CD34+ cells of SSC vs anti-GPA fluorescence gated on R3 to allow gating on GPA- (R4) or GPA+ (R5) and lower panel is representative scattergram of FSC vs 7-AAD fluorescence gated on R4, showing 7-AADbright (late apoptotic), 7-AADdim (early apoptotic), and 7-AAD- (viable) within CD71+ GPA- cells on day 3 of differentiation. (D) Cell-cycle distribution of mock-, control shRNA-, and MASL1-knockdown CD34+ cells at day 3, 5, 7, and 14 of EPO-induced differentiation analyzed by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. The data are expressed as mean percentage of sub G0/G1, G0/G1, S, and G2/M phase cells. Error bars represent the SD from 3 independent experiments; *P < .05. (E) Representative histogram for data presented in D.