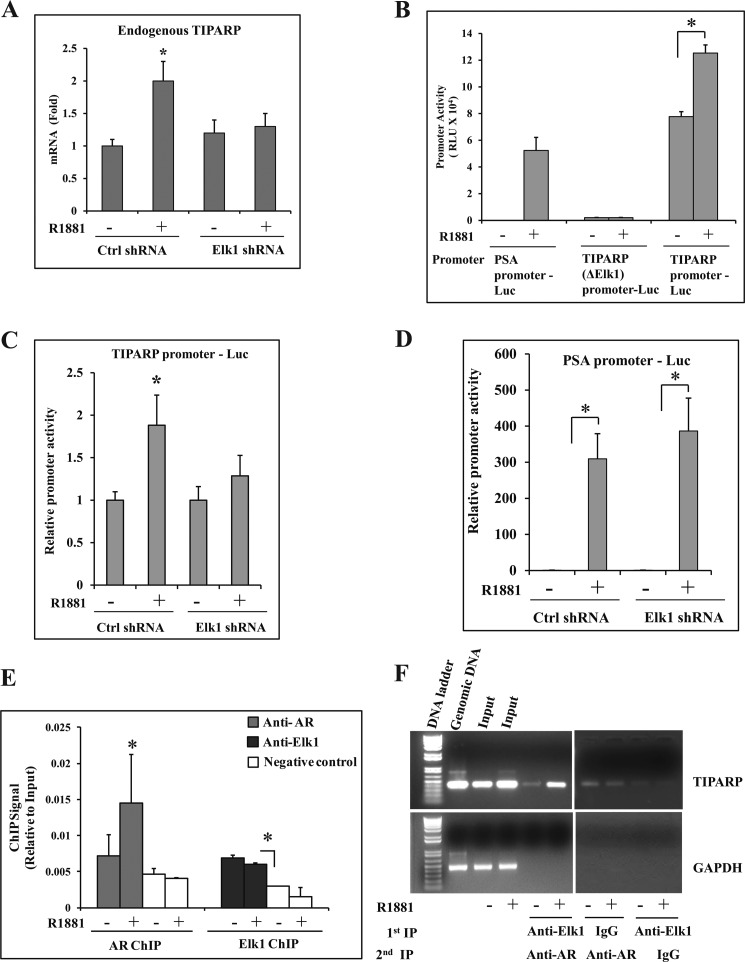
FIGURE 8.
Functional association of ELK1 and AR in the TIPARP gene promoter. A, LNCaP cells plated in hormone-depleted medium were infected with either ELK1 shRNA or control (Crtl) shRNA lentivirus. 72 h later, cells were treated with either vehicle or R1881 (1 nm) for 48 h. Total RNA from the cells was used to measure the relative mRNA levels for the endogenous TIPARP gene by real time quantitative RT-PCR. B, LNCaP cells plated in hormone-depleted medium were nucleofected with PSA promoter-Luc, TIPARP (ΔELK1) promoter-Luc, or TIPARP promoter-Luc. The cells were treated with either vehicle or R1881 (1 nm) for 48 h. The cells were then harvested, and the luciferase activities were measured. C and D, LNCaP cells plated in hormone-depleted medium were nucleofected with TIPARP promoter-Luc (C) or PSA promoter-Luc (D) and co-transfected with control shRNA or ELK1 shRNA lentivirus. The cells were treated with either vehicle or R1881 (1 nm) for 48 h. The cells were then harvested, and the luciferase activities were measured. E, LNCaP cells plated in hormone-depleted medium were treated with either vehicle or R1881 (1 nm) for 2 h. Cells were harvested and subjected to ChIP using either anti-AR antibody or anti-ELK1 antibody. TaqMan probes were used to quantify the immunoprecipitated chromatin. F, LNCaP cells plated in hormone-depleted medium were treated with either vehicle or R1881 (1 nm) for 2 h. Cells were harvested and subjected to ChIP using either anti-ELK1 antibody or normal rabbit IgG. The chromatin complexes from the first ChIP (1st IP) were subjected to re-ChIP (2nd IP) using anti-AR antibody. The immunoprecipitated chromatin was amplified by PCR using primers specific for the TIPARP gene promoter or a genomic sequence of GAPDH (non-targeting negative control). PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis on a 1% gel. Untreated genomic DNA was used as a control to ensure the specificity of the PCR amplification. *, p < 0.001. Error bars represent S.D. RLU, relative luciferase units.