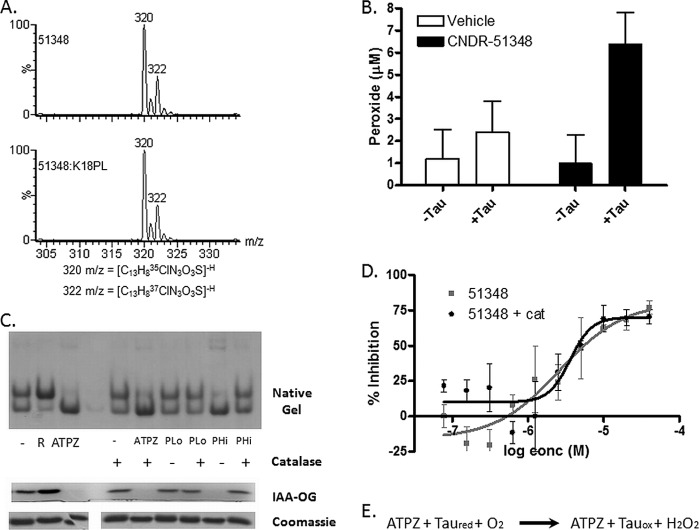
FIGURE 6.
ATPZs facilitate molecular oxygen-mediated cysteine oxidation. A, HPLC-MS analysis of CNDR-51348 that was incubated for 1 h at 37 °C in the absence (51348) or presence of K18PL (51348:K18PL). The molecular mass of the compound was unchanged after oxidation of Tau. The two major m/z values (320 and 322) correspond to CNDR-51348 containing the naturally occurring 35Cl and 37Cl isotopes. B, CNDR-51348 or vehicle (water) were incubated for 1 h in the absence or presence of K18PL followed by the determination of peroxide concentrations in the incubation mixtures. C, K18PL was left untreated (−) or was pre-reduced (R). In addition, K18PL was treated with CNDR-51348 or with 20 μm (PLo) or 1 mm (PHi) hydrogen peroxide for 1 h at 37 °C in the presence or absence of catalase. The samples were subsequently analyzed by native gel electrophoresis or underwent reaction with IAA-OG followed by SDS-PAGE to evaluate the extent of cysteine oxidation. Both the IAA-OG fluorescence and corresponding Coomassie blue staining are shown for each IAA-OG-treated sample. D, fibrillization reactions were conducted with K18PL in the presence of CNDR-51348 (51348) or the presence of both CNDR-51348 and catalase (51348 + cat). E, shown is the proposed reaction scheme of ATPZ-mediated oxidation of Tau.