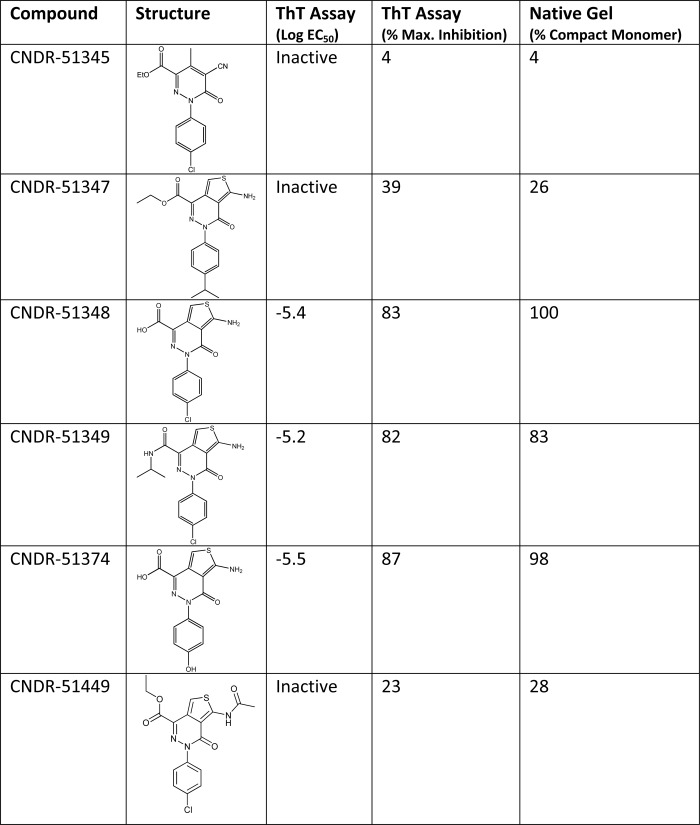
TABLE 1.
The relative activity of various ATPZ compounds in a 4-R Tau fibrillization reaction correlates with their ability to induce a disulfide-containing tau compact monomer
K18PL Tau fibrillization was monitored in the absence and presence of ATPZs using ThT fluorescence as previously described (26, 27). Compound activity is expressed both as the inhibitory log EC50 and as the maximum percent inhibition of Tau fibrillization. The compounds were also evaluated for their ability to induce the faster migrating, disulfide-containing compacted form of K18PL observed by native gel electrophoresis, as in Fig. 2B.