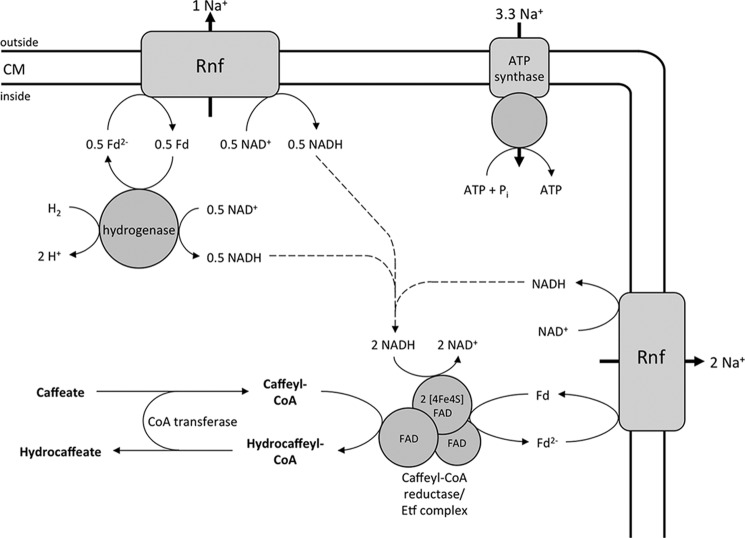
FIGURE 8.
Enzymology and bioenergetics of hydrogen-dependent caffeate respiration in A. woodii. The electron-bifurcating hydrogenase reduces ferredoxin (Fd) and NAD+ simultaneously. The Rnf complex couples the exergonic electron transfer from reduced ferredoxin to NAD+ with the translocation of Na+ ions. The electron acceptor caffeyl-CoA is reduced by the caffeyl-CoA reductase-Etf complex with NADH, which is coupled to the endergonic reduction of ferredoxin with NADH. The reduced ferredoxin is re-oxidized at the Rnf complex. The electrochemical Na+ gradient drives ATP synthesis by the Na+ F1F0-ATP synthase. The hydrocaffeyl-CoA:caffeate-CoA transferase CarA uses hydrocaffeyl-CoA to activate caffeate to caffeyl-CoA; this energy-saving CoA loop provides the regeneration of the acceptor under steady-state conditions. Initially, caffeate is activated by the caffeyl-CoA synthetase CarB at the expense of ATP (not shown). CM, cytoplasmic membrane.