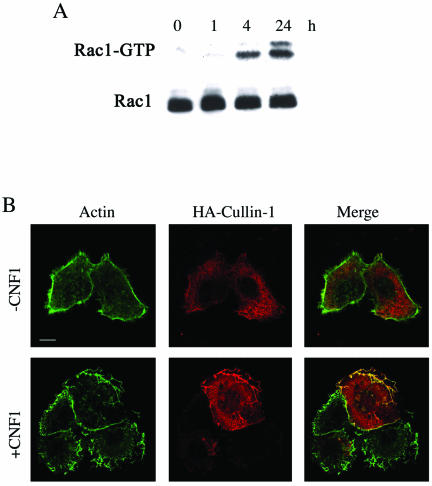
Figure 1.
Rac activation induces the relocalization of Cullin-1 to membrane ruffles. (A) Immunoblot showing the amount of activated Rac after different times of CNF1 exposure in HEp-2 cells, obtained by pulldown experiments. CNF1 induces a sustained activation of Rac that remains activated up to 24 h of toxin exposure. In parallel, total cell lysates were used to verify the equal amount of the Rac GTPase subjected to pull-down experiments. (B) Confocal microscopy analysis of control (-CNF1) and treated HEp-2 cells (+CNF1). From left to right, the first column shows the actin cytoskeleton, the second shows cells transfected by HA-Cullin-1, and the third is the merge of actin and Cullin-1. The toxin clearly promotes the recruitment of Cullin-1 to the actin-rich membrane ruffles. Bar, 10 μm.