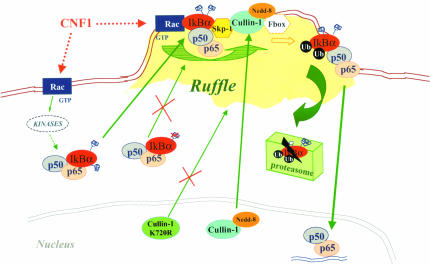
Figure 9.
Hypothetical model by which Rac activation instructs NF-κB transactivation in HEp-2 cells. In cells challenged with CNF1, activated Rac relocalizes to membrane ruffles where it promotes the grouping of the SCF complex (Skp-1, Cullin-1, F-box) and p50/p65/IkBα, probably functioning as a docking molecule. Neddylation of Cullin-1 that occurs in the nucleus allows the displacement of Cullin-1 to the SCF complex in the ruffle, whereas lack of neddylation (as in the case of the mutant Cullin-1 K720R) forces Cullin-1 to remain inactive in the nucleus. Phosphorylation of IkBα (occurring via specific kinases) is mandatory to target the ruffles. In fact, IkBα impaired in its capacity to link Pi, is unable to localize to the plasma membrane. Hence, at the level of the ruffles, phosphorylated IkBα is ubiquitinated. Its subsequent proteosomal degradation frees p50/p65 to enter the nucleus and activate transcription. Dotted lines indicate molecules or steps that have not been investigated in the present work, and their presence in the scheme derives from literature data.