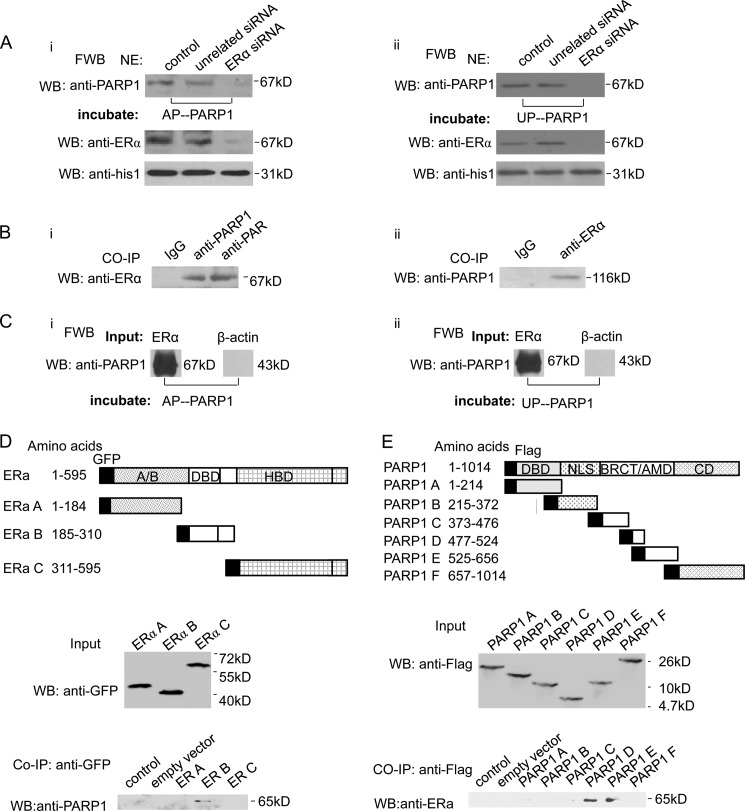
FIGURE 2.
ERα interacts directly with PARP1. A, VSMCs were transfected with ERα siRNA (50 nm) or unrelated siRNA (50 nm). After 48 h, nuclear extracts (NE) from VSMCs were analyzed by far-Western blot (FWB) (described under “Experimental Procedures”). After denaturation and SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, separated proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Membranes were incubated with UP-PARP1 protein (i, 1 μg/ml) or AP-PARP1 protein (ii, 1 μg/ml), and then detected with anti-PARP1 Ab. Western blot assay with anti-ERα Ab showed the efficiency of ERα siRNA. B, co-immunoprecipitation assay of PARP1-bound proteins or poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated proteins from non-treated VSMCs, followed by Western blot assay using anti-ERα antibody (i). Co-immunoprecipitation assay of ERα-bound proteins from VSMCs, followed by Western blot assay using anti-PARP1 antibody (ii). Nonspecific IgG served as negative control. C, in a cell-free system, the binding of ERα protein to UP-PARP1 protein (i) or AP-PARP1 protein (ii) was analyzed by far-Western blot (described under “Experimental Procedures”). β-Actin protein was used as negative control. D, diagram of GFP-tagged human ERα with its domains. Fragments A–C with their amino acid coordinates are listed. Co-immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated specific binding of ERα to the DBD of ERα. E, diagram of Flag-tagged human PARP1 with its domains, DBD, nuclear localization signal (NLS), BRCA1 C terminus (BRCT)/automodification domain (AMD), and catalytic domain (CD). Fragments A–F with their amino acid coordinates are listed. Co-immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated specific binding of ERα to the BRCT/AMD of PARP1. The results are from three independent experiments.