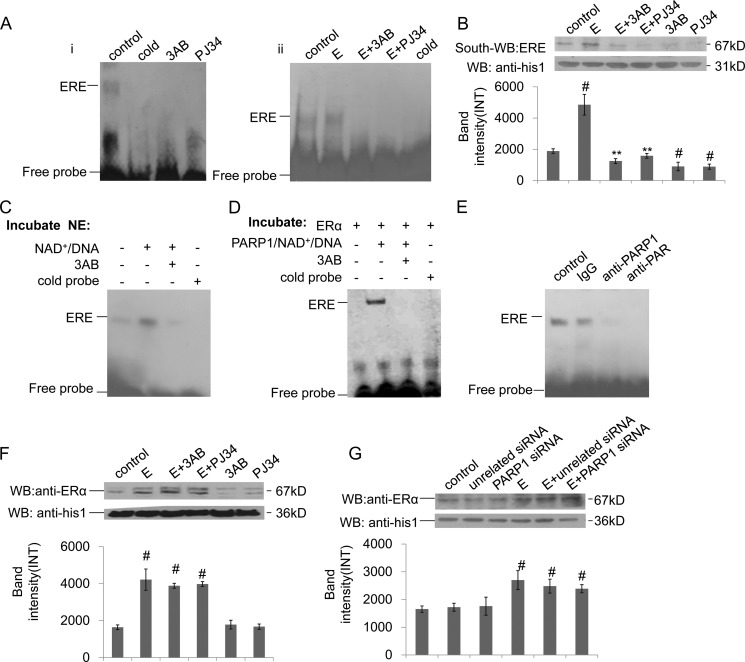
FIGURE 4.
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation promotes ERα binding to ERE in the nucleus. A, binding of ERα to ERE was detected by EMSA assay. (i) VSMCs were treated with 3AB (10 mm, 24 h) or PJ34 (10 mm, 24 h). (ii) VSMCs were treated with 3AB (10 mm, 24 h) or PJ34 (10 mm, 24 h) in the presence of estradiol (E, 10−7 m, 24 h). B, binding of ERα to ERE was detected by Southwestern blot assay. VSMCs were treated with 3AB (10 mm, 24 h) or PJ34 (10 mm, 24 h) in the absence or presence of estradiol (E, 10−7 m, 24 h). C, nuclear extracts from non-treated VSMCs were incubated with vehicles, PARP1/NAD+/active DNA, or PARP1/NAD+/active DNA/3AB, respectively. Binding of ERα to ERE was detected by EMSA assay. D, in a cell-free system, recombinant ERα protein was incubated with vehicles, PARP1/NAD+/active DNA, or PARP1/NAD+/active DNA/3AB, respectively. Binding of ERα to ERE was detected by EMSA assay. E, supershift assay was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Nuclear extracts from non-treated VSMCs were incubated with anti-PAR Ab, anti-PARP1 Ab, or vehicles. F, nuclear expression of ERα was detected by Western blot assay. VSMCs were treated with 3AB (10 mm, 24 h) or PJ34 (10 mm, 24 h) in the absence or presence of estradiol (E, 10−7 m, 24 h). G, nuclear expression of ERα was detected by Western blot assay. VSMCs were transfected with PARP1 siRNA (50 nm, 48 h) or unrelated siRNA (50 nm, 48 h), followed by treatment with estradiol (E, 10−7 m, 24 h). Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E. #, p < 0.05 and ##, p < 0.01 are for comparison with control group. *, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01 are for comparison with estradiol group (E).