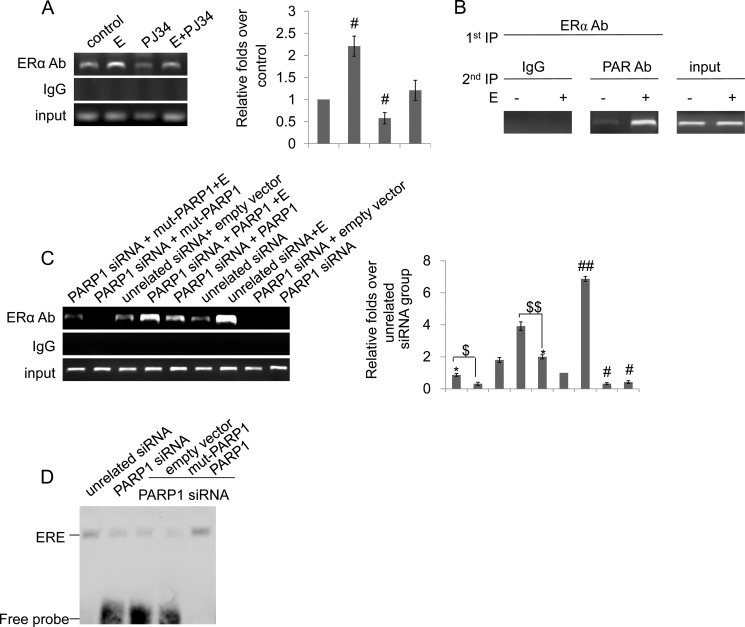
FIGURE 5.
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation enhances ERα recruitment to the IGF-1 promoter. A, ChIP-PCR assay using anti-ERα antibody for amplification of IGF-1 promoters in VSMCs. Cells were treated with estradiol (E, 10−7 m, 24 h), PJ34 (10 mm, 24 h), or E+PJ34. B, in re-ChIP assays, chromatin was first immunoprecipitated with anti-ERα antibody and then, re-immunoprecipitated with anti-PAR antibody or IgG. C, ChIP-PCR assay using anti-ERα antibody for amplification of IGF-1 promoters in VSMCs. Cells were transfected with PARP1 siRNA (50 nm) or unrelated siRNA (50 nm) for 24 h, and then were treated with empty vector (p3flag-CMV), full-length (hPARP1) or the plasmid expressing an enzymatically inactive PARP1 protein (mut-PARP1) for 48 h in the absence or presence of estradiol (E, 10−7 m). D, binding of ERα to ERE was detected by EMSA assay. VSMCs were transfected with PARP1 siRNA (50 nm) or unrelated siRNA (50 nm) for 24 h, and then were treated with empty vector (p3flag-CMV), full-length (hPARP1), or the plasmid expressing an enzymatically inactive PARP1 protein (mut-PARP1) for 48 h. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E. In Fig. 5A, #, p < 0.05 is for comparison with control group. In Fig. 5C, #, p < 0.05 and ##, p < 0.01 are for comparison with unrelated siRNA group. *, p < 0.05 is for comparison with PARP1 siRNA group. $$, p < 0.05 is for the indicated comparison.