Figure 1.
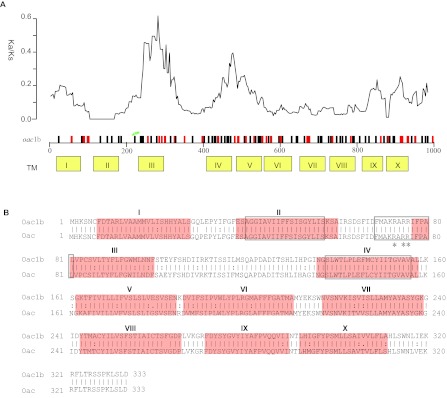
Comparison of protein Oac1b and Oac. (A) Plot of variation between Oac1b and Oac. Nucleotide differences were plotted across the horizontal axis with synonymous and non-synonymous mutations plotted as black and red vertical lines. Ticks and numbers across the horizontal axis are base positions. Transmembrance (TM) segments as predicted by Verma et al. are shown in yellow boxes below the gene. The critical residues for Oac function are indicated by green stars. The ratio of non-synonymous and synonymous substitution rate (Ka/Ks) across the gene using a sliding window of 90 bases (30 codons) and overlap of 3 bases (1 codon) is shown above the gene. (B) Pair-wise list the amino acid sequences of protein Oac1b and Oac. Lines represent amino acid residues that are identical, whereas dots represent amino acids that are similar. TM segments are indicated in red color. The three major regions conserved among the inner membrane trans-acylase family proteins are boxed. The three critical residues for Oac function are marked by asterisk.
