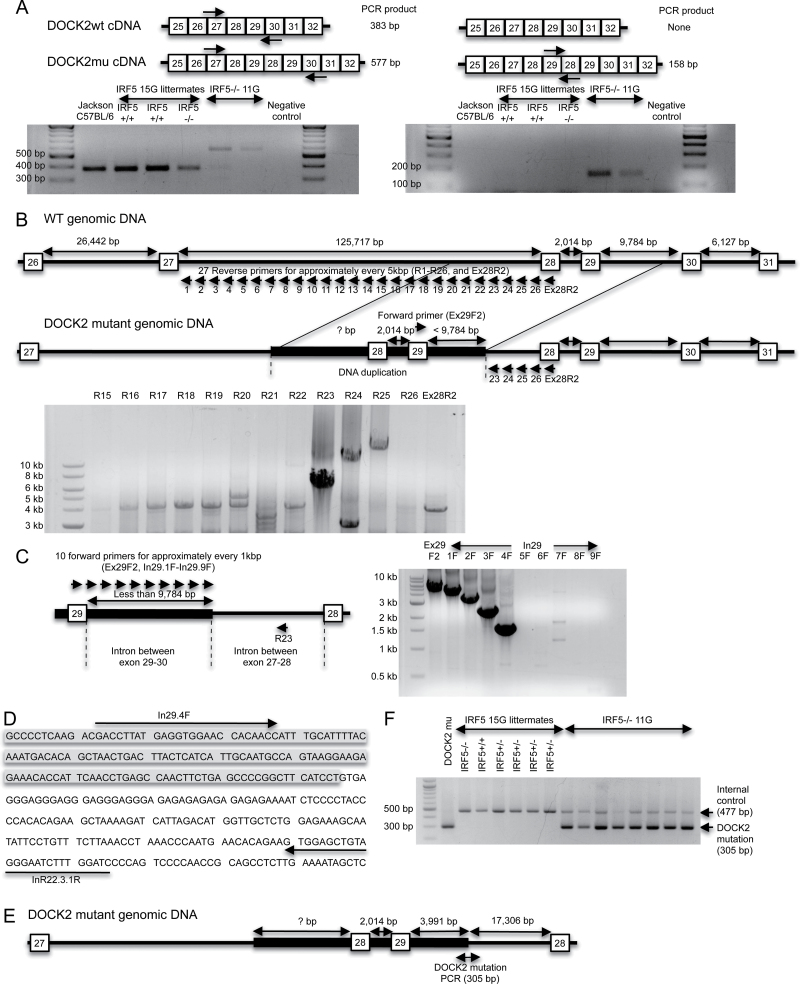
Fig. 2.
A DOCK2 mutation is detected in IRF5 −/− mice backcrossed 11 generations to C57BL/6 (IRF5 −/− 11G) mice but not in IRF5 −/− mice backcrossed 15 generations to C57BL/6 (IRF5 −/− 15G). (A) RT–PCR to detect the DOCK2 mutation (DOCK2mu). RNA was purified from splenic B cells of wild-type C57BL/6 mice from The Jackson Laboratory (Jackson wild-type), IRF5 +/+ and IRF5 −/− 15G littermates and IRF5 −/− 11G mice. RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA and amplified using specific primers to detect the exon 28–29 duplication as described (31). Primers used in the left-hand gel give a 577-bp product for the DOCK2 mutation and a 383-bp product for wild-type DOCK2. Primers used in the right-hand gel give a 158-bp product for the DOCK2 mutation and do not amplify wild-type DOCK2. (B) The diagram shows the hypothesized differences in genomic DOCK2 DNA between wild-type and DOCK2 mutant IRF5 −/− mice. In the DOCK2 mutant mice, the duplicated exon 28 and 29 together with some flanking DNA is inserted into the intron between exons 27 and 28. The gel shows a PCR performed using a forward primer, which recognizes exon 29 (Ex29F2) and 27 reverse primers (R1-R26 or Ex28R2), which detect the region in the intron between exons 27 and 28 that is closest to exon 28. PCR products were obtained with the R23–R25 primers. IRF5 −/− 11G genomic DNA containing the DOCK2 mutation was used as the template. (C) PCR was performed using the R23 reverse primer and 10 forward primers, which recognize either exon 29 (Ex29F2) or the intron between exons 29 and 30 (In\.1F to In29.9F). (D) DNA sequence of the 3′-end of DOCK2 mutation. The shaded region is the duplicated intronic sequence between exons 29 and 30, and the unshaded region is the non-duplicated intron between exons 27 and 28. (E) Diagram of the DOCK2 mutation. The duplicated segment of the DOCK2 gene present in the DOCK2 mutation ends at 3991bp after exon 29. This duplicated segment is inserted into intron 27–28 at 17 306bp before exon 28. (F) PCR to detect the DOCK2 mutation. Genomic DNA from IRF5 −/− 11G mice gave a PCR product for the DOCK2 mutation (305bp), whereas DNA from IRF5 +/+ and IRF5 −/− 15G littermates did not. CD19 PCR was used as an internal control to verify the adequacy of DNA preparation in each sample.