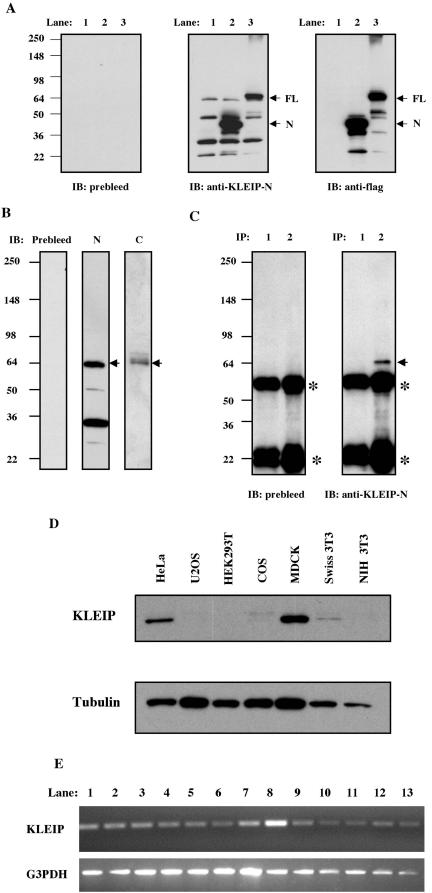
Figure 2.
KLEIP is a 64-kDa protein and expressed ubiquitously in human adult tissues. (A) Immunoblotting analysis using an affinity-purified anti-KLEIP-N antibody. FLAG-vector (lane 1), FLAG-tagged KLEIP-N (lane 2) or -FL (lane 3) was transfected in COS cells. Cell lysates (30 μg of protein) were separated on 8–16% gradient SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by the immunoglobulin fraction of preimmune sera (prebleed), purified anti-KLEIP-N antibody or anti-FLAG antibody. Predicted molecular sizes of KLEIP-N and -FL are 64- and 98-kDa, and the locations of these proteins are shown by arrows. Locations of molecular size markers are shown on the left of the panel. (B) Identification of endogenous KLEIP in cultured cells. Lysates of HeLa cells were analyzed by immunoblotting. Prebleed, N and C show immunoblots with the preimmune sera (for anti-KLEIP-N), anti-KLEIP-N or -C, respectively. The location of the predicted KLEIP is shown by an arrow. (C) Immunoprecipitation of KLEIP. HeLa cell lysates (390 μg of protein) were immunoprecipitated by 0.25 μg of the IgG fraction of preimmune sera (lane 1) or anti-KLEIP-N antibody (lane 2), followed by immunoblotting with IgG of preimmune sera or affinity-purified anti-KLEIP-N antibody. An arrow denotes the 64-kDa protein. Asterisks show bands of heavy and light chains of IgG. (D) Identification of endogenous KLEIP in cultured cells. Lysates (10 μg of protein in each) were separated by SDS-PAGE gels and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-KLEIP-N. Tubulin was detected as a loading control (bottom). (E) mRNA expression of KLEIP in human tissues. PCR was performed to detect expression of KLEIP (top) or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase G3PDH (bottom). Lane 1, heart; 2, brain; 3, liver; 4, placenta; 5, lung; 6, kidney; 7, skeletal muscle; 8, pancreas; 9, spleen; 10, thymus; 11, small intestine; 12, testis; 13, ovary; and 14, colon.