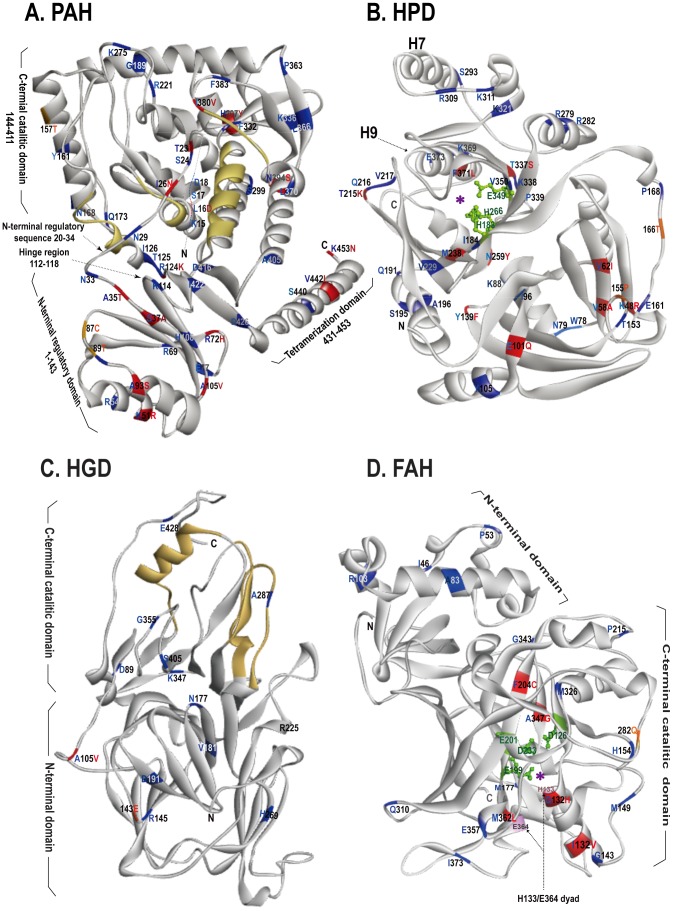
Figure 5. Stereoview of PAH, HPD, HGD, and FAH.
Amino acid residues that are conserved in all hibernators of bats but are different or diverged among non-hibernators of bats are indicated in red or blue, respectively. Orange color denotes positions that are conserved in all non-hibernating bats but diverged among hibernating bats. N-terminus and C-terminus are labeled as N and C, respectively. (A) The catalytic domain of PAH consisting of residues R131-L137, L250-R253, D316-W327, and E377-I380 is colored in yellow. The autoregulatory region is located between G20 and G34 at the N-terminus. Residues R112-T118 located in the hinge region are essential for phenylalanine-modulated proteolytic cleavage, and residues L431-K453 are required for the formation of a fully active enzyme tetramer. (B) Activity cave of HPD is indicated with a purple asterisk. Green color denotes residues and side chains of H183, H266, and E349 for binding metal ions and water molecule. (C) The active site of HGD composed of residues F282-T299, P320-K327, and M368-K385 is colored in yellow. Residue H269 is critical for trimerization of HGD and activation of the enzyme. (D) The purple asterisk denotes the activity cave of FAH. Green color indicates residues and side chains of D126, E199, E201, and D233 for Ca2+ binding. The H133/E364 dyad is critical for the catabolism of enzyme substrate.