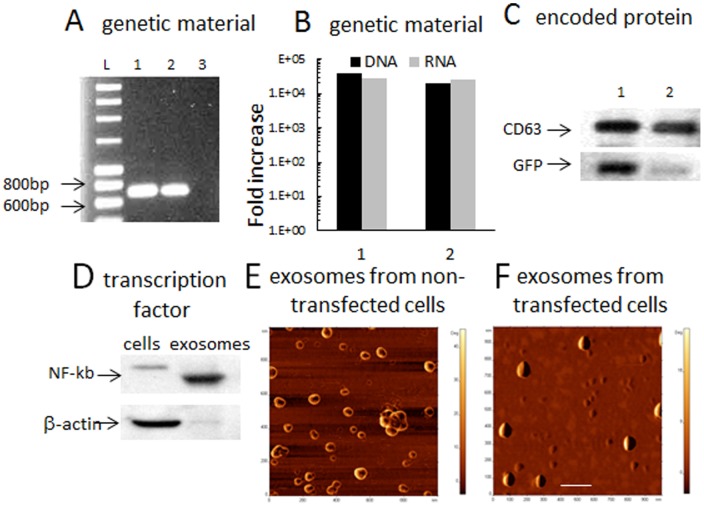
Figure 5. Exosomes secreted from GFP-transfected macrophages contain GFP DNA, RNA, the transcription factor, and expressed protein.
Exosomes from GFP-transfected cells were collected over two days and evaluated for (A): GFP DNA (1) and RNA (2) by PCR analysis. Exosomes secreted from macrophages transfected with empty vector were used as a control (3). (B): Levels of GFP DNA and RNA in exosomes from GFP-transfected macrophages were compared to those from empty vector-transfected macrophages (1), or non-transfected cells (2) by Real-Time PCR analysis. C: expression levels of GFP (30K) in exosomes from GFP-transfected cells (1) or empty vector-transfected macrophages (2) were examined by western blot and compared to the levels of CD63 (53K). Exosomes released from GFP-transfected macrophages contained four orders of magnitude more of GFP DNA and RNA compared to non-transfected macrophages or those transfected with empty vector (A, B); and 6.1 times greater levels of the expressed protein, GFP (C). Exosomes contain substantially higher levels of NF-kb, a transcription factor that involved in GFP pDNA expression, compared to macrophages as demonstrated by western blot (D). AFM images of exosomes revealed differences between: (E) small donut-shaped (empty) exosomes released from non-transfected macrophages, and (F) large spherical (likely filled with the expressed proteins and genetic material) exosomes from catalase-transfected macrophages. The bar: 200 nm.