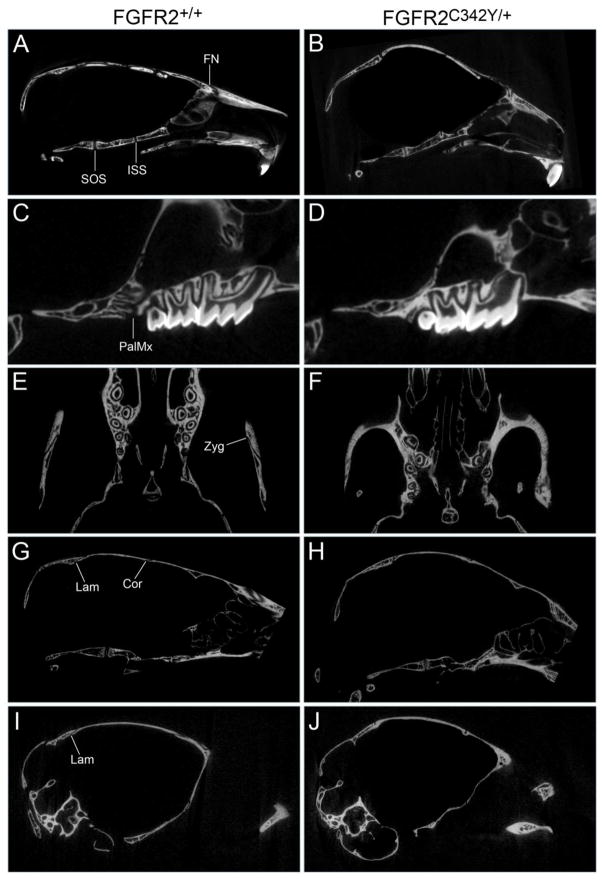
Fig. 4. Craniofacial bone fusions in BALB/c FGFR2C342Y/+ mice involve both cranial and facial bones.
Micro computed tomographic images of calvaria from four week old mice were viewed in axial, sagittal and coronal planes scanning the entire image to establish fusion or patency between adjacent bones. Images show premature fusion of the presphenoid and basisphenoid bones of the anterior cranial base, premature fusion of the frontal and nasal bones in FGFR2C342Y/+ (B) but not FGFR2+/+ (A) mice, and no fusion of the basisphenoid and basioccipital bones of the posterior cranial base in FGFR2C342Y/+ or FGFR2+/+ mice. Fusion between the maxillary and palatine bones, and of the bones of the zygomatic arch was also evident in FGFR2C342Y/+ (D,F) but not in FGFR2+/+ (C,E) mice. Fusion between the parietal and intraparietal bones was not found in either FGFR2C342Y/+ (H) or FGFR2+/+ (G) mice while fusion between the occipital and squamosal bones was evident in FGFR2C342Y/+ mice (J) but not in FGFR2+/+ mice (I). Fusion between the parietal and frontal bones was also evident in FGFR2C342Y/+ (H) but not FGFR2+/+ (G) mice. Fusion of paired parietal bones was not apparent in any of the mice (not shown). SOS: Spheno-occipital synchondrosis suture (located between basisphenoid and basioccipital bones); ISS: Intersphenoidal synchondrosis suture (located between presphenoid and basisphenoid bones); FN: frontonasal suture (located between frontal and nasal bones); PalMx: palatomaxillary suture (located between palatine and maxillary bones); Zyg: zygomatic arch sutures (located between squamosal, zygomatic and maxillary bones); Lam: lambdoid suture (located between intraparietal and parietal bones along top of cranium, located between occipital and squamosal bones along inferior edges of suture); Cor: coronal suture (located between frontal and parietal bones).