Fig. 5. Consistent pattern of premature craniofacial bone fusions in BALB/c FGFR2C342Y/+ mice.
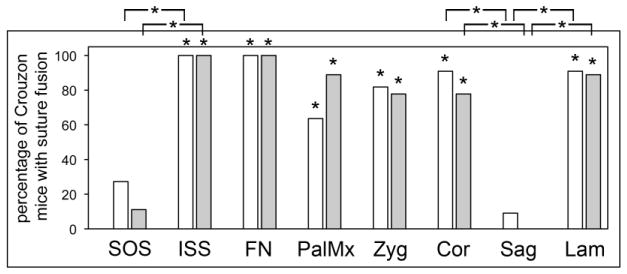
Percentage of BALB/c FGFR2C342Y/+ mice with fusion of indicated sutures is shown. Statistical analysis on the number of identified fused and patent sutures was performed to establish statistical significance between genotypes and genders, and to establish significance between sutures. No statistically significant differences were found for fusion of any of the analyzed sutures by gender, regardless of genotype. Results demonstrate a consistent pattern of bone fusion in BALB/c FGFR2C342Y/+ mice that primarily involves sutures involving bones of the neural crest lineage. The spheno-occipital synchondrosis and the sagittal sutures were not fused to a significant extent in the FGFR2C342Y/+ mice, while the intersphenoidal synchondrosis, coronal and lambdoid sutures were fused to a significant extent in the FGFR2C342Y/+ mice, when compared to wild type littermates. The nasofrontal suture, the palatomaxillary suture and bones of the zygomatic arch were also fused to a significant extent in FGFR2C342Y/+ compared to wild type mice. *p<.005 vs. percentage of fused FGFR2+/+ sutures, or between indicated sutures.
