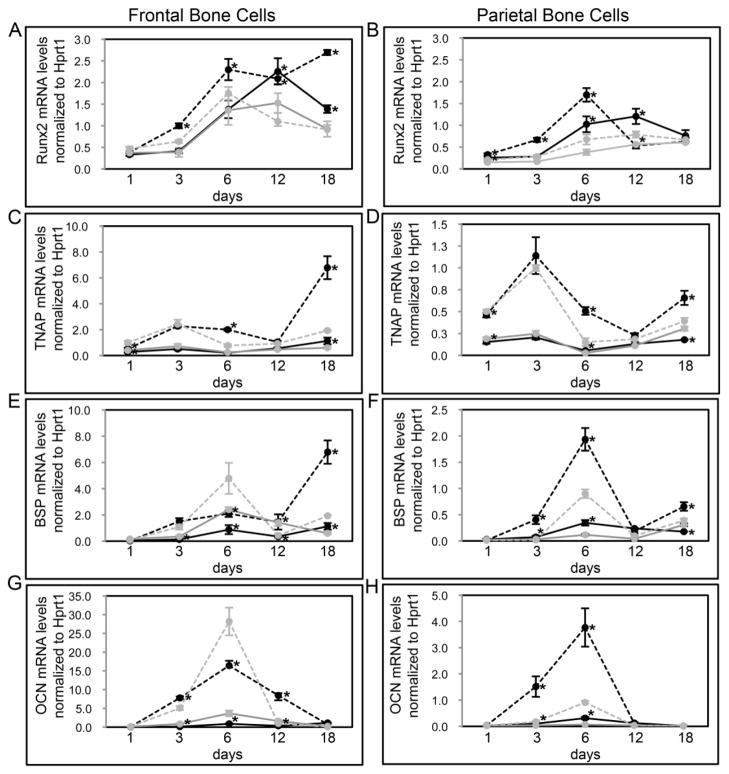
Fig. 8. FGFR2C342Y/+ mutation induces cranial bone specific changes in osteoblastic gene expression.
(A–H) Primary cells were isolated from FGFR2C342Y/+ and wild type, frontal (A,C,E,G) and parietal (B,D,F,H) bones then cultured with or without ascorbate to induce osteoblast differentiation. RNA was isolated at indicated time points. Osteocalcin (OCN), bone sialoprotein (BSP), tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) and Runx2 mRNA levels were measured by real time PCR. Results are presented as normalized to Hprt1. *p<.05 vs. WT. Note: all parietal cell mRNA levels are significantly lower than frontal cell mRNA levels, regardless of genotype (p<.05). Grey lines indicate cells cultured without ascorbate; black lines indicate cells cultured with ascorbate; dashed lines indicate FGFR2C342Y/+, solid lines indicate FGFR2+/+.