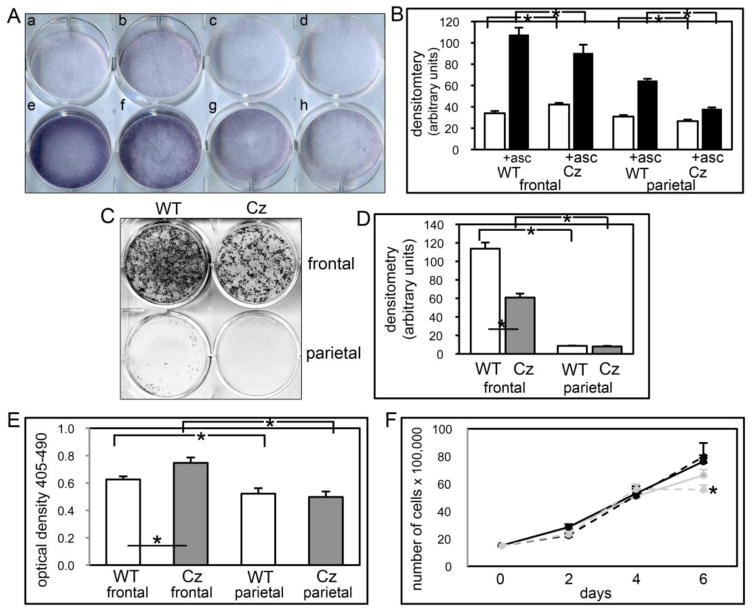
Fig. 9. FGFR2C342Y/+ mutation induces cranial bone specific changes in mineralization, apoptosis and proliferation.
(A,B) Primary cells were cultured with or without ascorbate to induce osteoblast differentiation. TNAP enzyme activity was visualized by incubation of cells with a colorimetric substrate. Enzyme activity was quantified by densitometry. Results are shown as means +/− standard deviations of triplicate experiments. (C,D) Cells were cultured with ascorbate and b-glycerophosphate to induce mineralized nodule formation. Mineralized nodules were stained by Von Kossa and quantified by densitometry. *p<.05 vs. WT. (E) Cells were cultured with 0.5% serum to induce apoptosis. Generation of apoptotic changes in DNA was assayed by a colorimetric reaction. Results are shown as means +/− standard deviations of quadruplicate experiments. (F) Cells were cultured without ascorbate for up to six days. Cells were stained with trypan blue and counted at indicated time points. Results are shown as means +/− standard deviations of sextuplet experiments.