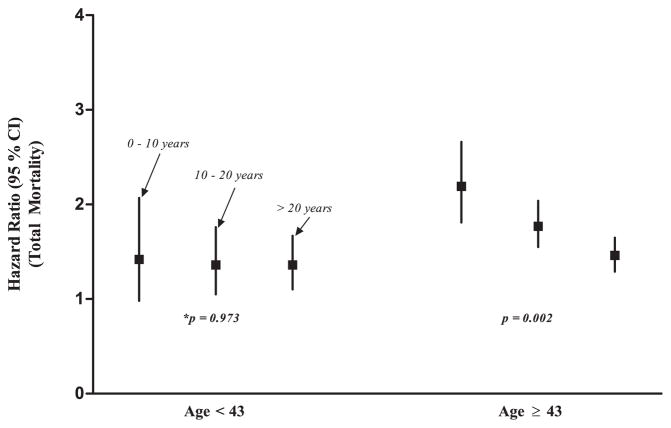
Figure 2.
Multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios for low fitness and total mortality across 0 to 10 years, 10 to 20 years, and >20 years of follow-up, stratified by age <43 or ≥43. Men and women were combined, and models were adjusted for sex, as well as age, systolic blood pressure, serum total cholesterol, body mass index, triglycerides, current smoking (yes/no), and diabetes (yes/no). P<0.05 suggests that the strength of the association between fitness and total mortality was different across the follow-up periods.