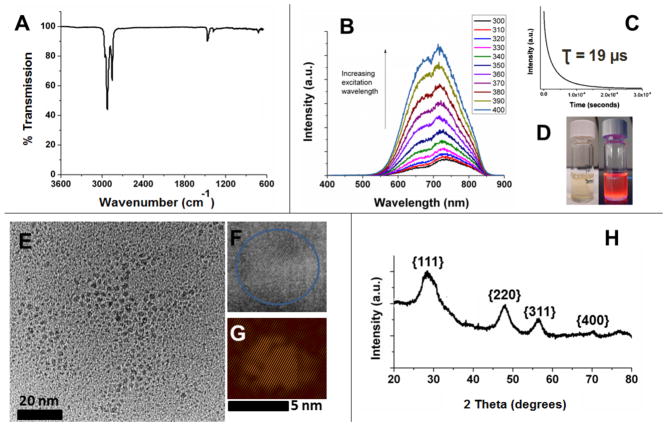
Figure 1.
A summary of the characterization of dodecyl terminated Si NCs (Si NC-A) derived from HSQ. (A) FT-IR spectrum drop-coated from a toluene solution. (B) Photoluminescence (PL) spectra of a toluene solution excited at indicated wavelengths. (C) Photoluminescence decay used to determine excited state lifetimes upon exciting with the 349 nm laser. (D) Toluene dispersions of dodecyl terminated Si NCs under ambient (left) and UV irradiation (right). (E) Bright-field transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of ca. 3.5 ± 0.4 nm diameter NCs (F) High-resolution transmission electron micrograph showing fringes of 0.33 nm characteristic of the Si{111} lattice spacing.. (G) The inverse Fourier transform of the HRTEM image in F (performed using DigitalMicrograph software). (H) X-ray powder diffraction pattern. Reflections have been indexed to those of the Si diamond structure. The particle size was determined to be ca. 3 nm by Scherrer analysis.