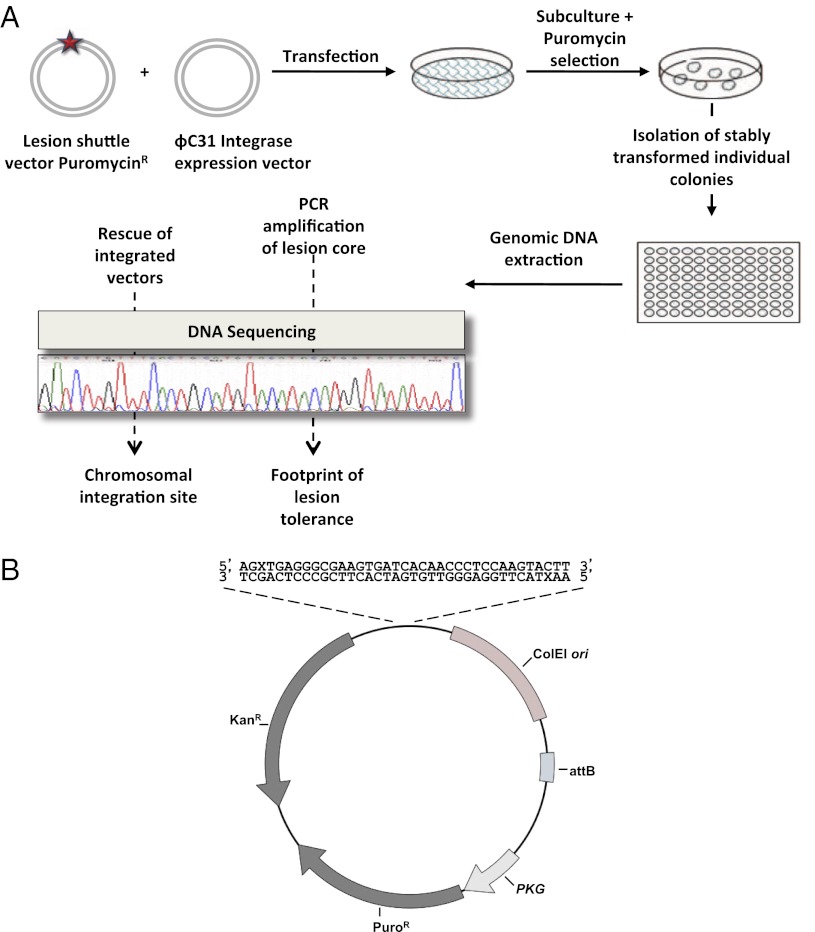
Fig. 2.
Outline of the DNA damage tolerance assay in chromosomes of mammalian cells. (A) Cultured cells were cotransfected with the lesion shuttle vector and the ϕC31 expression plasmid. In parallel, cells were transfected with a similarly constructed control plasmid without a lesion. Forty-eight hours after transfection the cells were subcultured, and after 24 additional hours they were subjected to puromycin selection. Approximately 14 d later resistant colonies were counted, picked, and individually transferred into a 96-well plate for further growth. When they reached suitable confluence, the cells in each individual well were harvested, and their chromosomal DNA was extracted. This DNA was used as a template in PCR reactions aimed to amplify the lesion core area. Amplified samples were then subjected to DNA sequence analysis. (B) Structure of the lesion shuttle vector pLSV5L. PuroR, puromycin resistance gene under the phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) promoter; attB, phage ϕC31 integrase attachment site; kanR, kanamycin resistance gene; X stands for a lesion. Two lesions in the staggered configuration are shown.