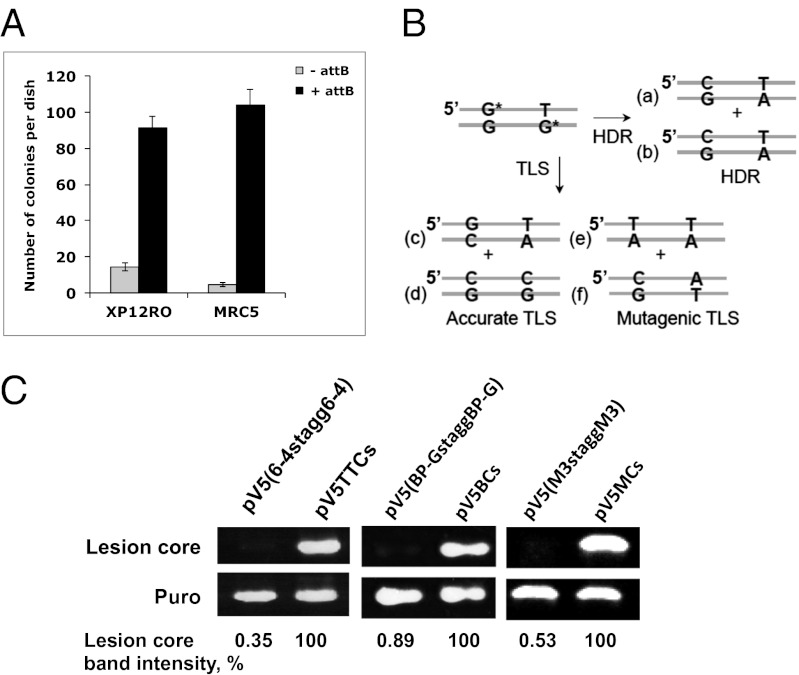
Fig. 3.
(A) Effect of ϕC31-integrase activity on the efficiency of plasmid integration into the chromosomes of mammalian cells. Human XP12RO and MRC5 cells were cotransfected with a mixture of the integrase expression vector pKGϕC31-int and pLSV5 (black bar) or pLSV5nA (gray bar) that lacks the integrase recognition sequence attB. Following transfection the cells were grown under puromycin selection for 12 d, until visible colonies were formed. Culture plates were then fixed and counted. The results shown are an average of three different transfections. (B) Products expected from TLS and HDR of two staggered BP-G lesions during chromosomal DNA damage tolerance. (C) Persistence of DNA lesions in XPA cells. Human XP12RO cells were transfected with the lesion shuttle vectors pLSV5TT6-4stagg6-4, pLSV5BP-GstaggBP-G, pLSV5M3staggM3, or their corresponding control vectors (without lesions). The vectors were extracted from the cells 3 d after transfection and used as templates in PCR reactions aimed to amplify the region containing the lesions (lesion core) and in parallel PCR reactions aimed to amplify a fragment of the puromycin resistance gene (puro) as an internal reference. Quantification of the images of the ethidium bromide-stained gel was done using ImageJ software. The percentage of the lesion-free background in each lesion shuttle vector is shown relative to the corresponding control vector with no lesion (100%), normalized to the intensity of the “puro” bands for each plasmid.