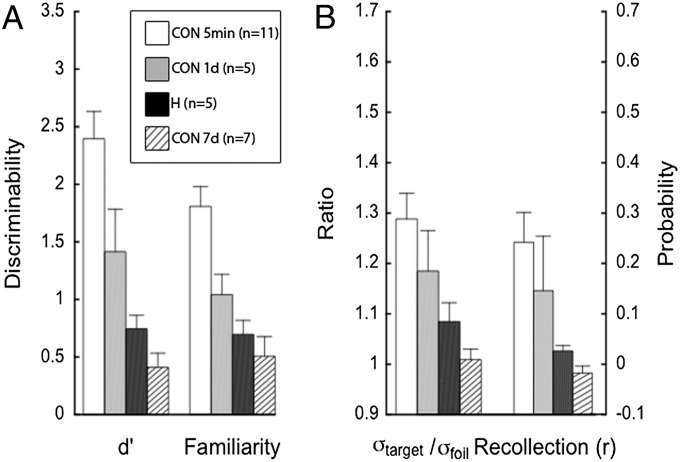
Fig. 3.
Parameter estimates for recognition performance of controls tested 1 or 7 d after learning (CON 1 d, n = 5; CON 7 d, n = 7) based on two models. Corresponding estimates from Fig. 1 for controls (CON, n = 11) and patients with hippocampal lesions (H, n = 5) tested 3 min after learning are shown for comparison. At 1 d after learning, control performance was numerically better than performance of the patients tested 3 min after learning whereas, at 7 d after learning, control performance was numerically better than that of patients. The DPSD model yields estimates of familiarity, d′ (A) and a probability estimate labeled recollection, r (B). The UVSD model yields d, a discriminability estimate (A) and the ratio of the SD of the target distribution to the SD of the foil distribution, σtarget/σfoil (B). All parameter estimates were higher for controls tested at 1 d after learning than for patients tested after 3 min. This pattern was reversed when controls were tested after 7 d. Error bars show SEM.